Sterile manufacturing remains one of the highest-risk areas in pharmaceutical production. EU and FDA inspection data consistently show that 30–40% of critical GMP observations in sterile facilities relate to contamination control, environmental monitoring failures, or aseptic process weaknesses. These findings reinforce why Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) play a central role in sterility assurance and regulatory oversight across the pharmaceutical industry.
As a result, Annex 1 has become a central inspection reference for sterile manufacturing sites, placing operations under sustained regulatory scrutiny and significantly raising expectations for audit readiness across Europe and global supply chains.
Within this context, companies can no longer treat sterile manufacturing guidance as a static requirement. Instead, inspection-ready compliance now requires proactive risk management, integrated contamination control, and demonstrable operational control throughout aseptic operations.
Table of Contents
What Is EU GMP Annex 1 and Why It Matters for Sterile Manufacturing
EU GMP Annex 1 defines the core regulatory expectations for the manufacture of sterile medicinal products. It sets detailed requirements for aseptic processing, environmental control, cleanroom design, personnel practices, and sterility assurance throughout the product lifecycle.
Following its major revision, inspectors now apply sterile manufacturing requirements with a much stronger focus on risk-based decision-making, documented scientific justification, and system-level integration rather than checklist-driven compliance. As a result, companies must demonstrate not only that controls exist, but also that they function together effectively during routine operations.
Because sterile products bypass many downstream safety barriers, regulators directly link aseptic control requirements to patient safety and product integrity. Consequently, inspection outcomes often depend on how consistently organisations translate these expectations into daily manufacturing practice under real operational conditions.
Scope of Sterile Manufacturing Requirements
This regulatory framework applies broadly across sterile manufacturing activities. Inspectors expect companies to clearly define how requirements apply within their operations, including:
- Sterile injectable and infusion products
• Ophthalmic and inhalation products
• Terminally sterilised and aseptically manufactured products
• Cleanroom and controlled environment operations
• Sterile component preparation and filling activities
Clear scope mapping reduces inspection ambiguity and demonstrates structured compliance ownership.
Key Changes in the Revised Guideline
The revised guidance introduced several inspection-critical updates that now receive heightened regulatory attention:
- Mandatory implementation of a Contamination Control Strategy (CCS)
• Stronger focus on risk-based aseptic processing decisions
• Enhanced expectations for cleanroom classification and monitoring
• Clearer requirements for environmental monitoring programs
• Increased scrutiny of human intervention and operator behaviour
Inspectors increasingly assess not only whether controls exist, but whether companies can justify, integrate, and continuously review them.
Contamination Control Strategy (CCS) as the Core Requirement
The visual below shows how contamination control, aseptic processing, and sterile manufacturing controls connect under EU GMP expectations.
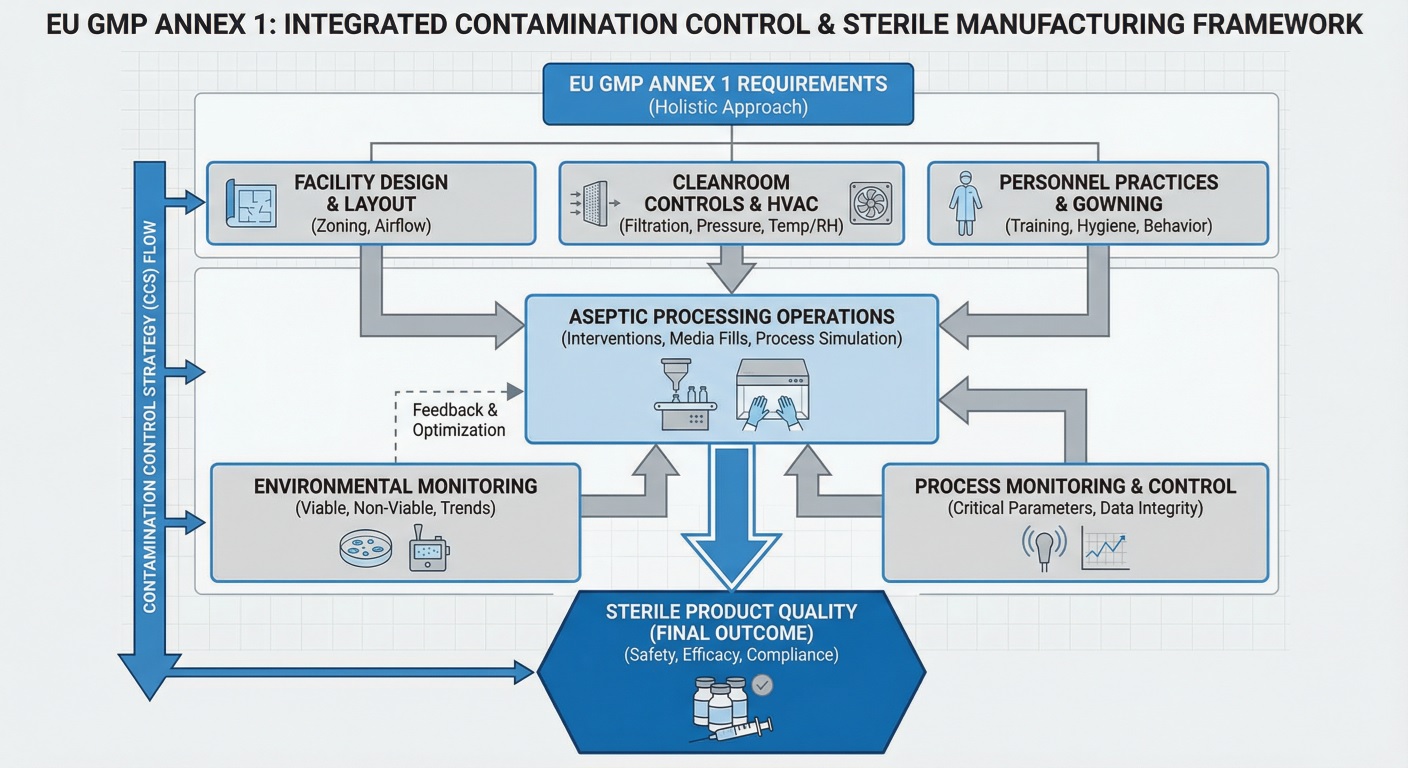
The Contamination Control Strategy sits at the heart of sterile manufacturing compliance. Regulators view the CCS as the central framework linking facility design, process controls, environmental monitoring, and operational discipline.
Rather than a standalone document, inspectors expect the CCS to function as a living system that actively guides sterile manufacturing decisions. In practice, inspectors look for evidence that contamination risks are understood at process level and that controls evolve as operations, equipment, and environments change.
A fragmented CCS often signals deeper quality system weaknesses. In contrast, a well-integrated strategy demonstrates maturity and inspection readiness.
What Inspectors Expect to See in a CCS
During inspections, authorities typically look for practical evidence that contamination control drives real-world decisions, including:
- Defined contamination risks and corresponding control measures
- Clear linkage between CCS, risk management, and process design
- Integration with environmental monitoring and cleanroom strategy
- Documented review cycles and change management
- Evidence that deviations feed back into CCS updates
When companies treat CCS as an operational tool rather than a compliance file, inspections become more predictable.
Annex 1 During GMP Inspections
Inspectors assess compliance holistically. They review documentation, observe behaviour, and test whether controls perform under routine conditions. They also compare inspection findings with historical trends to evaluate consistency over time. Repeated weaknesses, even if individually minor, often signal ineffective oversight and trigger deeper scrutiny of governance and management involvement.
Common inspection focus areas include:
- Aseptic process simulations and media fill performance
- Environmental monitoring trends and alert handling
- Cleanroom classification and requalification practices
- Operator training and gowning discipline
- Alignment between procedures and actual execution
Deficiencies often arise when systems exist on paper but fail under operational pressure. Therefore, audit readiness depends on consistency rather than perfection.
This diagram illustrates how key sterile manufacturing controls translate into inspection readiness and regulatory confidence.

Final word
Sterile manufacturing continues to attract intense regulatory attention. Inspection trend summaries from EU authorities and FDA Form 483 data show that contamination-related deficiencies account for a substantial share of critical and major GMP findings in sterile operations year after year. In several recent recall reviews, sterility assurance failures and environmental control breakdowns emerged as leading root causes of regulatory action, even in organisations with otherwise mature quality systems.
Against this backdrop, EU GMP Annex 1 functions as more than a regulatory guideline, it operates as a real-time stress test of sterile manufacturing control. Companies that embed its principles into daily decision-making, maintain a robust Contamination Control Strategy, and sustain inspection-ready discipline not only reduce regulatory risk but also protect patients and strengthen long-term regulatory trust.
FAQ
Inspectors assess how contamination risks are identified, controlled, and reviewed across aseptic operations involved in sterile medicinal product manufacturing. They focus on whether the contamination control strategy integrates with environmental monitoring data, deviation handling, and routine decision-making within regulated production environments.
Findings often arise from weak environmental monitoring trends, poorly justified aseptic interventions, unclear ownership of contamination risks, or gaps between approved GMP procedures and actual execution on the manufacturing floor.
Authorities expect risk-based reviews throughout the product lifecycle. Process changes, emerging trend signals, recurring deviations, or inspection feedback should trigger reassessment rather than reliance on fixed review schedules.
References

Mahtab Shardi
Mahtab is a pharmaceutical professional with a Master’s degree in Physical Chemistry and over five years of experience in laboratory and QC roles. Mahtab contributes reliable, well-structured pharmaceutical content to Pharmuni, helping turn complex scientific topics into clear, practical insights for industry professionals and students.

Master GxP Validation in 2026: Meaning, Key Steps, and Validated State Control
Auditors want evidence you can trace, not opinions you can explain. GxP validation links intended use, requirements, risk, and test results into one story. When you control changes and review performance, you keep the system inspection-ready every day on time.

Master GMP Compliance in 2026: Meaning, Core Elements, and How to Implement
GMP compliance keeps medicines safe, consistent, and traceable across every batch. This guide explains core GMP elements, practical rollout steps, and common pitfalls. It also shows how to strengthen training, documentation, data integrity, and audit readiness.

History of Pharmacovigilance: From the Thalidomide Crisis (1961–2026) to GMP Oversight
Thalidomide in 1961 changed drug safety forever. Since then, pharmacovigilance has grown from crisis response to proactive risk management. Today, teams track signals, tighten reporting rules, and connect safety data to quality systems. As a result, PV now links directly to GMP oversight, audits, and data integrity.


