More than 70% of regulatory observations in pharmaceutical manufacturing stem from quality system failures, according to inspection trend reports. In Malaysia, regulators increasingly apply lifecycle-based GMP oversight to protect patient safety and supply reliability. As a result, GMP functions as an active regulatory system rather than a checklist, requiring manufacturers to align daily operations with inspection expectations and ongoing compliance requirements.
Learn more about the global foundations of Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and their regulatory role.
Table of Contents
Regulatory Overview of GMP in Malaysia
The diagram below illustrates the structure of GMP compliance and regulatory oversight in Malaysia.
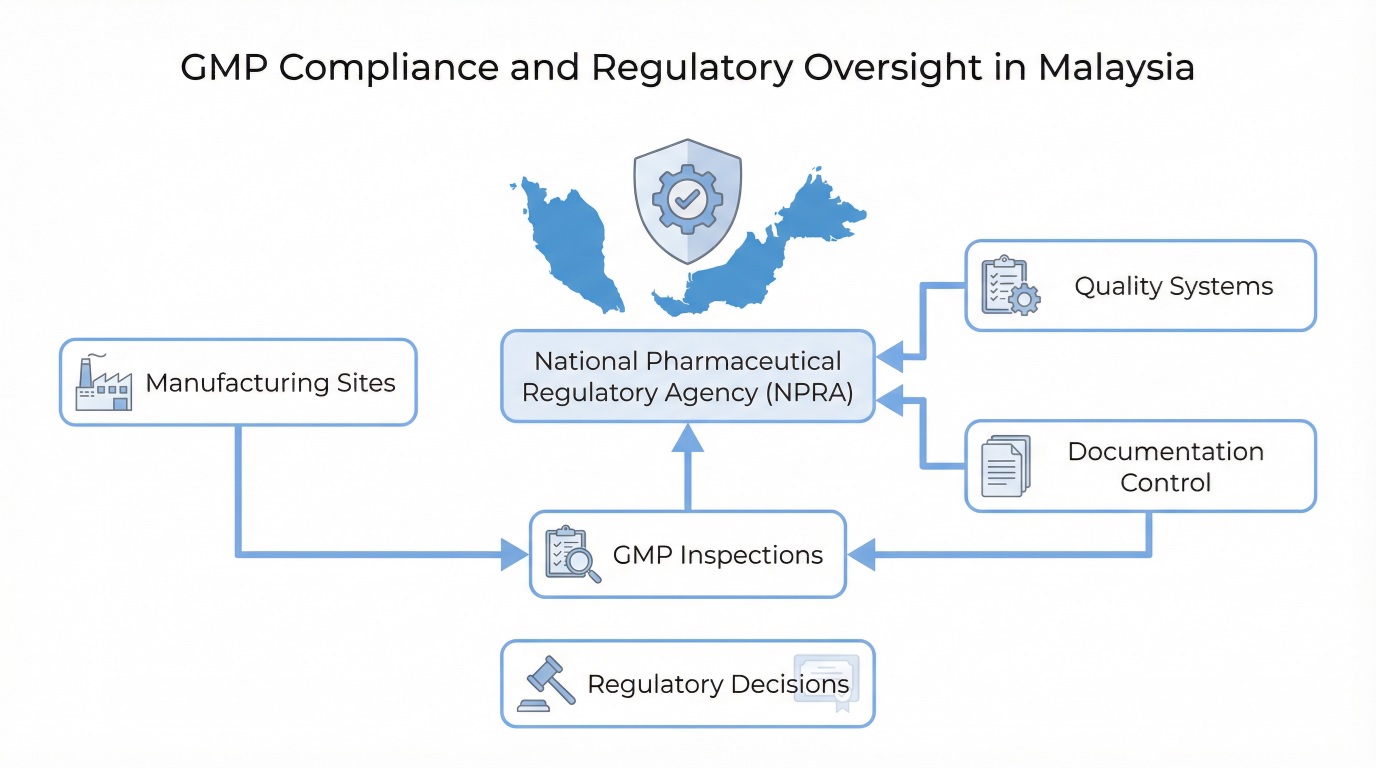
Malaysia regulates pharmaceutical manufacturing through a centralized national framework that emphasizes quality systems, risk control, and regulatory accountability. Authorities focus on whether processes remain under control during routine operations rather than relying on end-product testing alone.
This approach allows regulators to evaluate manufacturing performance across the entire production lifecycle. As a result, compliance depends on system maturity, staff competence, and documented evidence of control.
Role of the National Pharmaceutical Regulatory Agency (NPRA)
The National Pharmaceutical Regulatory Agency (NPRA) serves as the primary authority responsible for pharmaceutical regulation and manufacturing oversight. NPRA conducts inspections, assesses compliance status, and enforces corrective actions when manufacturers fail to meet expectations.
In addition, NPRA evaluates foreign manufacturing sites that supply products to Malaysia. Through these inspection and enforcement activities, GMP in Malaysia functions as a practical regulatory framework that directly influences manufacturing authorization, import approvals, and continued market access.
Legal Basis and Applicable GMP Guidelines
Regulatory authorities define manufacturing requirements through legally binding national regulations supported by detailed guidance documents. These documents align closely with ASEAN GMP principles and reflect internationally recognized manufacturing standards.
Key regulatory references generally include:
- National pharmaceutical legislation
- NPRA-issued GMP guidance
- ASEAN GMP standards used for regional harmonization
Together, these references establish a consistent compliance baseline for manufacturers.
Scope of GMP Application in Malaysia
Manufacturing requirements apply to a wide range of pharmaceutical activities. Authorities regulate facilities based on product type, process complexity, and intended market use.
Typically, GMP applies to:
- Finished pharmaceutical products
- Active pharmaceutical ingredients
- Certain regulated medicinal or health products
Because the scope remains broad, manufacturers must assess applicability early in facility planning and product development.
GMP Certification Process in Malaysia
The diagram below outlines the main steps in the GMP certification and inspection process in Malaysia.

The certification process follows a structured pathway that links documentation review with on-site verification. Regulators expect manufacturers to demonstrate readiness before inspections begin.
The process generally includes:
- Submission of an application and supporting documentation
- Regulatory assessment and inspection planning
- On-site inspection and system evaluation
- Regulatory decision and certification outcome
Each stage builds cumulative confidence in manufacturing control.
GMP Inspections and Compliance Expectations
During inspections, authorities assess how systems operate under real conditions. Inspectors focus on implementation rather than policy statements.
Inspection emphasis typically includes:
- Quality management systems
- Process validation and change control
- Personnel training and responsibilities
- Documentation accuracy and traceability
Therefore, inspection readiness depends on daily operational discipline.
Common GMP Deficiencies Observed During Inspections
Despite preparation, inspectors frequently identify recurring compliance gaps. These findings usually reflect weaknesses in systems rather than isolated mistakes.
Common deficiencies include:
- Incomplete or inconsistent records
- Weak deviation and CAPA management
- Poor change control execution
- Inadequate training documentation
Addressing these issues requires preventive quality strategies.
Documentation and Quality System Requirements
Documentation forms the backbone of manufacturing compliance. Regulators expect manufacturers to demonstrate control through accurate, legible, and traceable records.
Key documentation elements include:
- Standard operating procedures
- Batch manufacturing records
- Validation and qualification reports
- Deviation and corrective action records
Without reliable documentation, compliance claims lose credibility.
GMP Alignment With ASEAN and International Standards
Malaysia aligns its national GMP framework with ASEAN GMP to promote regulatory convergence and facilitate regional trade. This alignment helps reduce variability in inspection expectations and supports smoother cooperation among ASEAN member states.
In addition, Malaysia’s approach reflects globally accepted manufacturing principles used by major regulatory authorities. As a result, manufacturers that maintain local compliance also strengthen their international credibility and improve readiness for cross-border regulatory evaluations.
Download Guidance Document Here– Foreign GMP Inspection (NPRA)
Provides official NPRA expectations for GMP inspections of pharmaceutical manufacturing sites.
Why GMP Compliance in Malaysia Matters for Manufacturers
Manufacturing compliance directly influences regulatory approval, market confidence, and business continuity. Manufacturers that maintain system-level control reduce inspection risk and avoid costly disruptions.
Moreover, strong compliance performance supports competitiveness within ASEAN markets. As regulatory scrutiny increases, compliance becomes a strategic asset rather than a regulatory burden.
For this reason, robust national manufacturing standards play a central role in long-term manufacturing sustainability.
Final Words
Regulatory authorities conduct hundreds of manufacturing inspections each year across pharmaceutical facilities in the region. These inspections repeatedly demonstrate that compliance cannot rely on preparation alone. Instead, inspectors assess whether systems perform consistently over time.
Because of this reality, Good Manufacturing Practices in Malaysia require continuous attention, disciplined quality systems, and proactive oversight. Manufacturers that treat compliance as an ongoing responsibility remain better positioned to meet regulatory expectations and maintain market trust.
FAQs
Authorities enforce compliance through routine inspections, structured document reviews, and follow-up regulatory actions. These activities focus on how quality systems perform under real manufacturing conditions rather than on written procedures alone.
The National Pharmaceutical Regulatory Agency (NPRA) conducts GMP inspections and evaluates compliance for both domestic manufacturers and foreign production sites supplying regulated therapeutic products to the Malaysian market.
Alignment with ASEAN GMP standards enables manufacturers to meet shared regional expectations, simplifies regulatory cooperation, and supports smoother market access across ASEAN member states.
Inspectors primarily assess quality management systems, documentation integrity, deviation handling, change control, and manufacturing controls that directly impact product quality and patient safety.
Official GMP guidelines and regulatory PDFs are available through NPRA-related publications and national regulatory resources, which provide up-to-date clarification on compliance and inspection expectations.
References

Ershad Moradi, a Content Marketing Specialist at Zamann Pharma Support, brings 6 years of experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Specializing in pharmaceutical and medical technologies, Ershad is currently focused on expanding his knowledge in marketing and improving communication in the field. Outside of work, Ershad enjoys reading and attending industry related networks to stay up-to-date on the latest advancements. With a passion for continuous learning and growth, Ershad is always looking for new opportunities to enhance his skills and contribute to pharmaceutical industry. Connect with Ershad on Facebook for more information.

Master GMP Compliance in 2026: Meaning, Core Elements, and How to Implement
GMP compliance keeps medicines safe, consistent, and traceable across every batch. This guide explains core GMP elements, practical rollout steps, and common pitfalls. It also shows how to strengthen training, documentation, data integrity, and audit readiness.

History of Pharmacovigilance: From the Thalidomide Crisis (1961–2026) to GMP Oversight
Thalidomide in 1961 changed drug safety forever. Since then, pharmacovigilance has grown from crisis response to proactive risk management. Today, teams track signals, tighten reporting rules, and connect safety data to quality systems. As a result, PV now links directly to GMP oversight, audits, and data integrity.

Periodic Safety Update Reports (PSUR) in Pharmacovigilance: Regulatory Expectations and Inspection Impact in 2026
Periodic Safety Update Reports now function as inspection evidence, enabling regulators to evaluate ongoing safety surveillance, benefit–risk assessment, and pharmacovigilance system control across the product lifecycle, rather than treating PSURs as regulatory submissions.


