The pharma job market changes fast. Automation spreads across labs, plants, and offices, and AI now supports data review, documentation, and even safety signal detection. According to global workforce reports, up to 40–50% of work activities could be automated, while demand for social and emotional skills may rise by more than 20% this decade. In other words, technical expertise alone no longer protects your career. Because of this shift, companies look closely at pharma soft skills when they hire, promote, and build project teams.
Managers want people who communicate clearly, solve problems under pressure, and collaborate across QA, RA, PV, production, and IT. If you map your development with a structured pharma skill tree, you can see exactly which soft skills support your next role and which gaps to close first.
This article explains which pharma soft skills matter most in year, how they influence your growth in a highly regulated industry, and what you can do—starting today—to build them in a focused, strategic way.
Why Pharma Soft Skills Matter in 2026
The pharma landscape grows more complex every year. Regulations expand, guidelines update often, and global markets expect strict compliance. Therefore, professionals must combine technical knowledge with strong pharma soft skills.
First, regulatory complexity demands clear cross-functional communication. You work with QA, regulatory, R&D, production, marketing, and sometimes health authorities. Misunderstandings can delay submissions or even risk product quality. Recent industry guides highlight communication, collaboration, and critical thinking as top skills for pharma careers.
Second, AI tools now assist with signal detection, documentation, trial design, and manufacturing optimization. Yet AI still needs humans who can ask the right questions, interpret outputs, and make ethical decisions. Studies on AI and workforce skills emphasize adaptability, digital literacy, and social skills as key complements to automation.
Third, pharma companies move toward patient-centric models. Teams must understand patient needs, explain risks, and respond with empathy. Therefore, pharma interpersonal skills and pharma emotional intelligence now matter as much as scientific expertise.
Finally, cross-functional project teams are the norm. Complex launches need regulatory, medical, supply chain, and commercial teams to move together. Strong teamwork, negotiation, and leadership skills keep everyone aligned and on schedule.
Core Pharma Soft Skills Required in the Industry
Now let’s look at the core skills that employers expect in 2025 and beyond. These skills show repeatedly in job ads, hiring research, and industry career guides.
We will focus on four major groups:
- Communication skills pharma
- Adaptability and continuous learning
- Cross-functional collaboration and teamwork
- Problem-solving and critical thinking
Together, they support leadership, AI collaboration, and long-term career growth.


Communication Skills
Strong communication skills pharma roles depend on more than nice emails. You explain complex data, update busy stakeholders, and connect every decision to patient safety. Therefore, this set of pharma soft skills helps you reduce errors, speed up approvals, and build real trust across the company.
Key elements of strong communication in pharma include:
- Clear updates: Share short, structured messages with what, why, and next steps.
- Active listening: Ask questions, repeat key points, and confirm shared understanding.
- Simple language: Translate technical terms into words non-specialists understand.
- Audience awareness: Adjust tone and detail for QA, RA, PV, management, or patients.
- Visual clarity: Use clean charts, flows, and tables to highlight the main risk or trend.
- Feedback loops: Invite comments, summarise decisions, and document agreements quickly.
Adaptability & Continuous Learning
Regulations evolve. Digital tools change. New therapies reach the market. Therefore, adaptability now ranks among the most critical soft skills.
You need a mindset of continuous learning. Read new guidance, attend webinars, and test new tools regularly. Stay curious about AI, data dashboards, and digital quality systems. Moreover, recent research on future skills shows a clear trend: workers who embrace change keep their value as automation grows.
Practically, this means you:
- Try new workflows instead of defending old ones.
- Learn from small failures and adjust quickly.
- Seek feedback from peers and managers.
This attitude turns you into a “go-to” person for pilots and innovation projects.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Modern pharma work rarely happens in isolation. You cooperate with people from R&D, clinical, PV, quality, regulatory, supply chain, IT, and marketing. Therefore, cross-functional communication and teamwork count as essential behavioral competencies.
Good collaboration includes:
- Shared goals: Start every project with a common purpose and clear success criteria.
- Respect for roles: Acknowledge each function’s expertise and limits in every discussion.
- Structured updates: Use short stand-ups, clear minutes, and visual boards to align work.
- Ask for input early: Involve QA, RA, PV, and supply chain before decisions lock in.
- Transparent negotiation: Discuss trade-offs between speed, cost, and compliance openly.
- Resolve conflicts quickly: Address tension with facts, active listening, and patient-focused outcomes.
Negotiation skills also matter in many pharma roles. In project meetings, you balance speed, cost, and compliance. With clear arguments and empathy, teams reach decisions that protect patients and support business goals.
As AI tools connect data from many functions, collaboration will increase, not decrease. People who coordinate across functions will stay highly valuable.
Problem-Solving & Critical Thinking
Pharma projects always bring surprises: stability issues, data anomalies, inspection findings, or supply delays. Therefore, companies value problem-solving and critical thinking as core skills.
Start by defining the problem clearly. Next, collect facts and separate noise from real signals. Then question assumptions, run root-cause analysis, and design practical countermeasures. Additionally, calculate the impact on patients, timelines, and costs before you act.
Key elements of strong problem-solving and critical thinking include:
- Define the real problem: Separate symptoms from causes before you jump to solutions.
- Check the data: Use trends, logs, and reports to confirm what truly happens.
- Root-cause thinking: Apply tools like 5 Whys or fishbone diagrams to dig deeper.
- Risk-based decisions: Weigh impact on patients, compliance, and business before choosing actions.
- Structured action plans: Turn analysis into clear steps, owners, and due dates.
- Review and learn: After each fix, ask what you can improve next time.
Critical thinking also supports better use of AI. You check model outputs, compare them with real–world constraints, and challenge suspicious patterns. This human oversight protects against blind trust in algorithms and supports safer decisions.
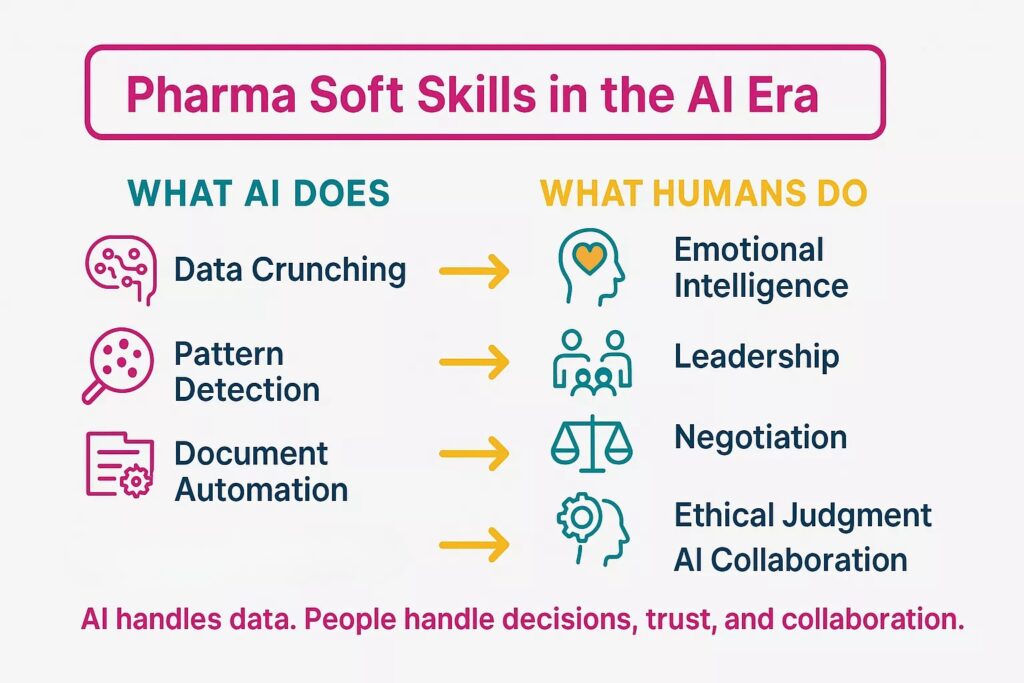
Soft Skills in the AI Era
AI reshapes every part of the pharma lifecycle. It supports discovery, clinical trial design, safety signal detection, and manufacturing. Yet, even as algorithms grow stronger, interpersonal skills grow more valuable, not less. You still make final decisions, explain complex risks, and protect patients’ trust.
Global reports show that up to 40–50% of work activities can be automated in many roles, but social, emotional, and higher-cognitive skills will see the strongest growth in demand this decade. At the same time, AI and analytics skills now rank among the fastest-growing requirements for pharma jobs. This shift means you must blend digital awareness with human strengths like judgment, empathy, and leadership.
Because of this, the most important soft skills in the AI era include:
- Emotional intelligence: With strong emotional awareness, you read team moods, manage tension, and protect psychological safety.
- AI collaboration mindset: In every project, you ask the right questions, test AI outputs, and turn insights into clear actions.
- Ethical judgment: When you decide, you weigh efficiency against patient safety, data privacy, and regulatory expectations.
- Strategic thinking: Strong strategy skills help you choose where to apply AI, redesign processes, and accept justified risks.
- Cross-functional communication: In cross-team work, you explain AI-driven results clearly to QA, RA, PV, clinicians, and management.
- Continuous learning habits: Over time, you update your skills, explore new tools, and stay ahead of automation trends.
When you intentionally develop these competencies, you do more than “coexist” with AI. You turn technology into a partner that amplifies your impact, supports better decisions, and helps you build a resilient career in a rapidly changing industry.
Recommended Learning Paths (Informal & Professional)
You can build interpersonal skills in many ways. You do not need to wait for a formal promotion or a big training budget. However, a mix of informal practice and structured learning works best.
Start with informal learning paths:
- Join cross–functional projects and volunteer for coordination roles.
- Ask for feedback after key meetings or presentations.
- Keep a reflection journal on communication wins and mistakes.
- Practice negotiation in small settings, such as workload planning.
Then add professional learning paths:
- Attend workshops on communication, leadership, and conflict management.
- Join webinars on AI in pharma and human–machine collaboration.
- Take online courses on critical thinking, emotional intelligence, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Final Words
The pharma industry in 2025 faces fast change, strict regulation, and growing AI usage. Technical expertise still matters. However, soft skills in the pharma industry now decide who progresses, who leads projects, and who stays resilient when markets shift.
Therefore, we treat communication, adaptability, cross-functional collaboration, and critical thinking as non-negotiable. Add emotional intelligence, ethical judgment, and AI collaboration to your toolkit. Then connect these skills to a clear learning path, for example through a pharma skill tree or a structured development plan.
If you invest in soft skills in pharmaceutical industry now, you do more than protect your job. You build a flexible, future-proof career that can adapt to new roles, new technologies, and new patient needs for many years to come.
Boost your pharma soft skills and technical expertise with Pharmuni
FAQ:
Soft skills in the pharma industry are human skills that support your technical knowledge. They include communication, teamwork, emotional intelligence, and problem–solving. Together, they help you work safely, clearly, and efficiently in regulated environments. Therefore, soft skills matter for every role, from lab to leadership.
Automation and AI now handle more routine tasks in pharma. However, people still make decisions, explain risks, and lead teams. Because of that, soft skills in the pharma industry now drive promotion and trust. Strong interpersonal skills keep you adaptable when tools, rules, and markets change.
In the AI era, you still need classic behavioral competencies like communication and teamwork. However, you also need AI collaboration, ethical judgment, and strategic thinking. You must question AI outputs and link them to patient safety and compliance. Therefore, your human judgment becomes even more valuable.
Most hiring managers look first at communication skills, teamwork, and reliability. Then they check your problem–solving mindset and critical thinking. They also value pharma interpersonal skills like empathy and respect. These skills show that you can work well in cross–functional, high–pressure situations.
References:

Stephanie Männicke
Digital Marketing Especialist at Zamann Pharma Support, brings 8 years of experience in Corporate and Digital Communication. Specializing in Digital Marketing and Content Creation, Stephanie is currently focused on creating strategic content for Pharmuni's networks, especially content on topics such as recruitment, onboarding and employer branding. Outside of work, Stephanie is a mum, a crocheter and a movie fan. An avid reader and in search of expanding her knowledge, Stephanie is always looking for ways to innovate communication in the digital environment and connect people in a genuine way.

Master GxP Validation in 2026: Meaning, Key Steps, and Validated State Control
Auditors want evidence you can trace, not opinions you can explain. GxP validation links intended use, requirements, risk, and test results into one story. When

Master GMP Compliance in 2026: Meaning, Core Elements, and How to Implement
GMP compliance keeps medicines safe, consistent, and traceable across every batch. This guide explains core GMP elements, practical rollout steps, and common pitfalls. It also

History of Pharmacovigilance: From the Thalidomide Crisis (1961–2026) to GMP Oversight
Thalidomide in 1961 changed drug safety forever. Since then, pharmacovigilance has grown from crisis response to proactive risk management. Today, teams track signals, tighten reporting


