Pharmaceutical manufacturing inspections increasingly depend on harmonised standards because regulators now operate under a global inspection framework. The Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-operation Scheme (PIC/S) currently comprises more than 50 participating authorities from Europe, Africa, the Americas, Asia, and Australasia, reflecting the scale of international Good Manufacturing Practices GMP cooperation. Participating regulators use shared guidance and inspector training to reduce inspection variability and support mutual confidence across borders, helping ensure more consistent GMP interpretation and follow-up expectations across regions.
Table of Contents
What Is the PICS Guide in a GMP Inspection Context
It is the inspection framework used by PIC/S authorities to align how GMP is interpreted and enforced across countries.
Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-operation Scheme (PIC/S) is a global regulatory cooperation framework, and the term PICS Guide is commonly used to describe the inspection principles, practices, and reference documents that support consistent GMP inspections among participating authorities. In a GMP inspection context, it functions as a shared basis for aligning inspection planning, inspector expectations, evidence evaluation, and follow-up decisions.
In simple terms: It helps inspectors assess pharmaceutical manufacturing sites using comparable standards, even when inspections are conducted by different authorities.
From an operational perspective, this alignment reduces variability in inspection outcomes by shifting the focus from local interpretation to harmonised inspection logic. Inspectors use this framework to determine whether pharmaceutical quality systems demonstrate sustained control under routine operating conditions not just compliance on paper.
Why GMP Inspection Harmonization Matters for Compliance Decisions
It reduces inspection variability by aligning how compliance evidence is interpreted.
GMP compliance challenges often arise when the same system is judged differently by different inspectors. This creates repeat observations that persist even after technical issues are addressed. The PICS Guide addresses this problem by promoting shared inspection logic, particularly around risk prioritisation, evidence evaluation, and deficiency classification.
It shifts inspections away from local style differences toward common expectations. For manufacturers, this has practical consequences. Quality leaders can focus remediation on system weaknesses that matter across inspections rather than reacting to individual preferences. Over time, this alignment supports more predictable inspection outcomes and reduces regulatory uncertainty during multi-site or international operations.
Core Principles of the PICS Guide Used During Inspections
Inspectors rely on a consistent set of principles to guide behaviour, judgement, and decision-making during GMP inspections across jurisdictions. Shared principles define what inspectors prioritise, how they assess evidence, and how findings are classified.
We will discuss:
- Risk-Based Inspection Approach
- Consistency and Harmonization of GMP Expectations
- Inspector Competency and Training Frameworks
- Inspection Reporting and Follow-Up Practices
Risk-Based Inspection Approach
Inspections are planned using risk signals rather than equal coverage of all systems. Inspectors concentrate on areas with the highest potential impact on product quality and patient safety, such as contamination control, data integrity, and lifecycle validation.
In practice, when risk indicators are identified, inspection scope often expands. A single documentation issue may trigger broader evaluation of governance, oversight, and CAPA effectiveness.
Consistency and Harmonization of GMP Expectations
Harmonisation reduces inspection variability by aligning how inspectors interpret GMP requirements. Rather than redefining compliance at each site visit, inspectors apply common criteria when assessing whether controls are adequate and sustained.
This principle is critical for global manufacturers. Systems that are defensible under harmonised expectations are less likely to generate repeat findings when inspected by different authorities.
Inspector Competency and Training Frameworks
Inspection outcomes depend on inspector capability as much as on site performance. PIC/S promotes structured training and qualification expectations to support consistent inspection judgement.
Micro-credibility: During inspections, experienced inspectors often test the same evidence pathways traceability, decision logic, and effectiveness checks regardless of location, reflecting shared training rather than individual preference.
Inspection Reporting and Follow-Up Practices
Inspection conclusions are structured to support comparability. Findings are classified using harmonised criteria, and follow-up actions focus on whether corrective measures address root causes and prevent recurrence.
This approach reinforces the idea that compliance is measured over time, not only at the moment of inspection.
How Inspectors Apply GMP Inspection Harmonization During Audits
During GMP audits, inspection outcomes are shaped by a structured sequence of risk-based planning, evidence evaluation, and harmonised interpretation rather than isolated checklist reviews.
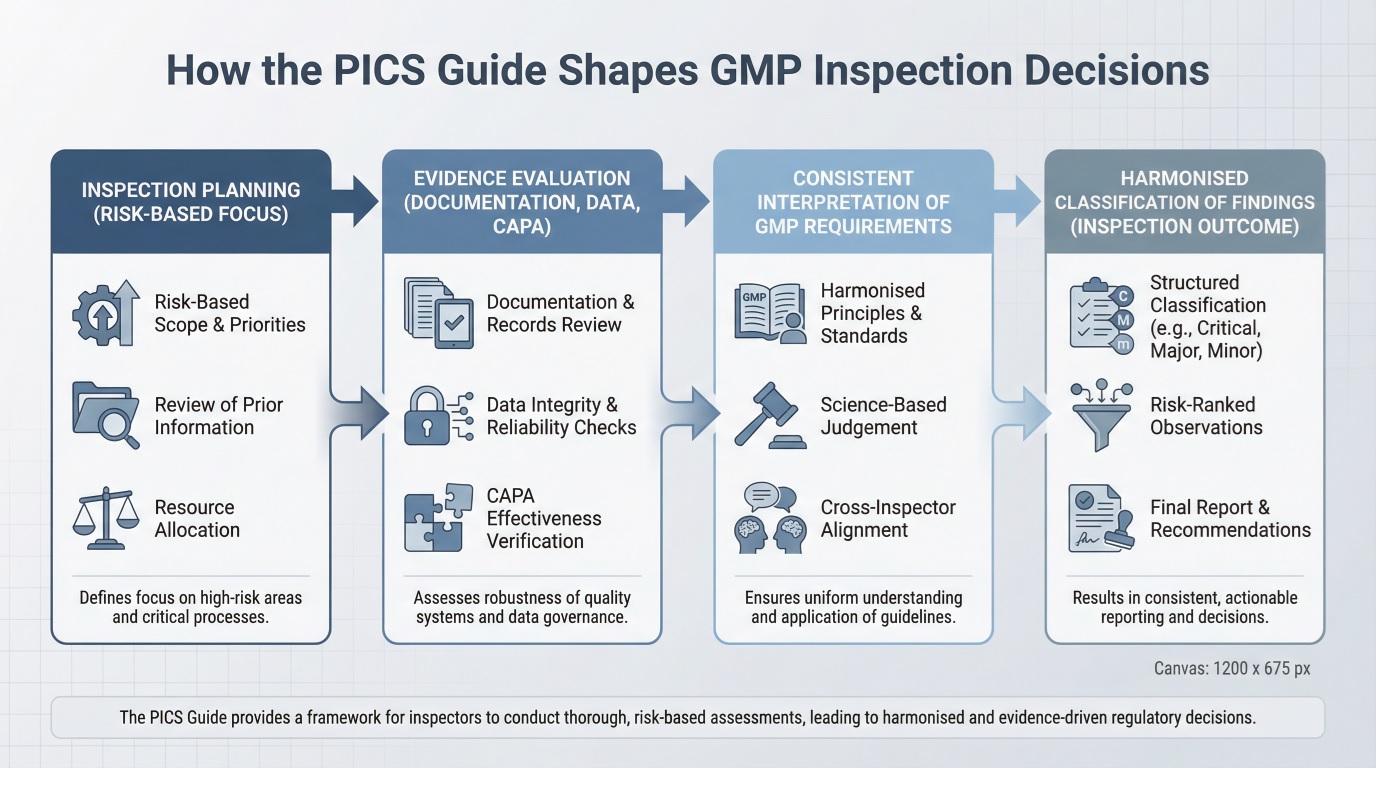
On site, inspectors evaluate whether pharmaceutical quality systems operate consistently under normal workload conditions. Evidence is reviewed across multiple dimensions, including batch documentation, deviation handling, data integrity controls, and management oversight.
GMP inspection harmonization shapes how inspectors connect these elements during audits. Weak documentation or delayed investigations are often interpreted as indicators of broader system fragility, even when facilities and equipment meet technical standards.
As a result, regulatory inspection readiness depends less on presentation and more on routine discipline: timely records, clear decision rationale, and demonstrable CAPA effectiveness.
PICS Guide Alignment with Global GMP Regulations
While GMP principles are globally aligned on paper, inspection outcomes have historically varied due to differences in interpretation, inspection depth, and enforcement thresholds across authorities.
The PICS framework addresses this gap by creating a shared inspection language reducing variability in how findings are assessed, classified, and followed up across regions.
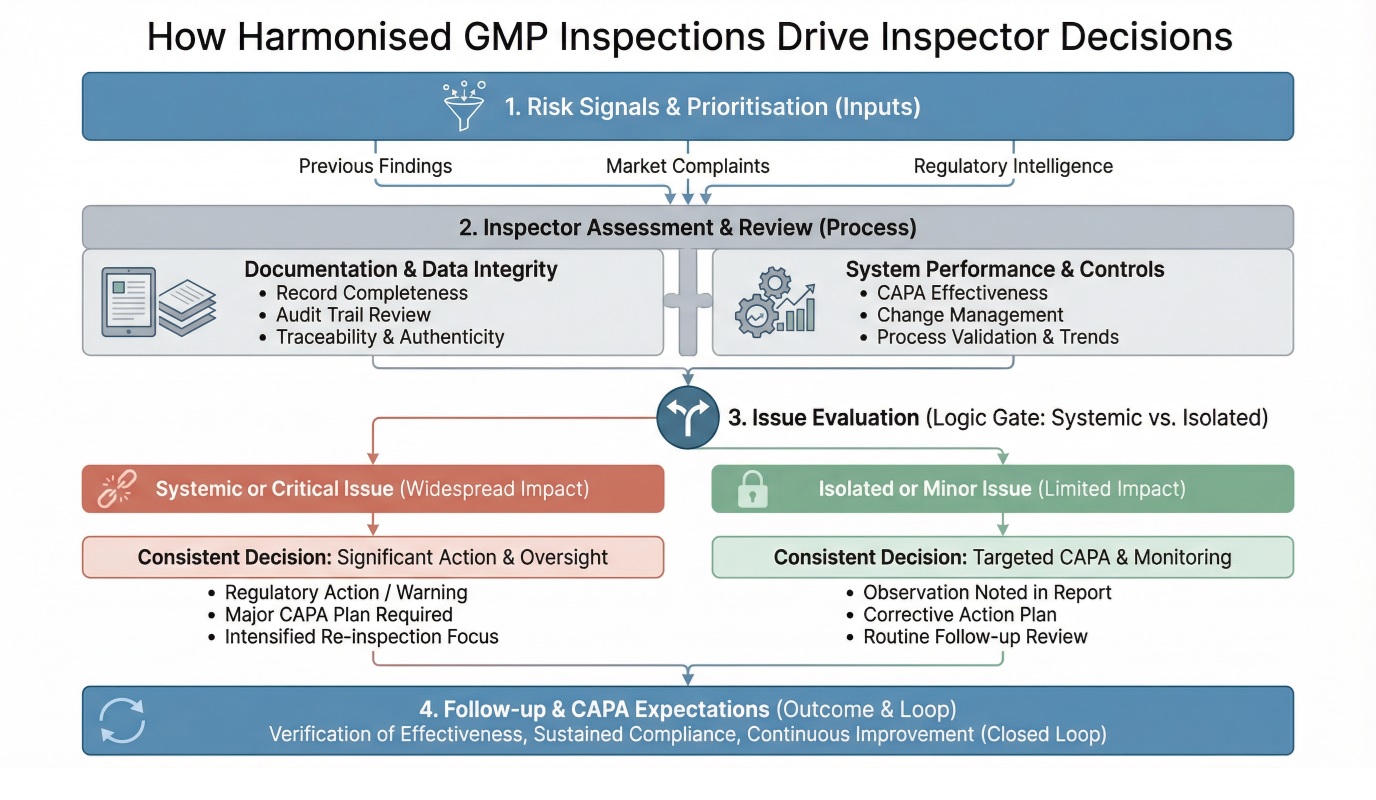
PIC/S operates alongside established GMP regulations rather than replacing them. Its role is to align how those requirements are inspected and enforced, supporting regulatory cooperation and mutual confidence between authorities.
For manufacturers, this alignment reduces friction when operating across regions. Quality systems designed around harmonised expectations are easier to defend during inspections and require fewer jurisdiction-specific adjustments. Over time, this consistency supports more efficient regulatory engagement and clearer compliance strategy.
Final Word
Recent PIC/S reporting confirms 56 participating authorities worldwide, reflecting the scale of cross-border inspection coordination and the practical need for harmonised inspection logic in global operations. Micro-credibility: In multi-site networks, repeated observations often persist not because teams ignore GMP, but because evidence, classification, and follow-up expectations differ across inspections creating rework cycles and extended CAPA closeouts.
Used correctly, the PICS Guide helps reduce repeat GMP observations driven by inconsistent interpretation, lowers inspection friction by clarifying what defensible evidence looks like, and reduces regulatory uncertainty when manufacturing, quality, and governance decisions must withstand scrutiny across multiple jurisdictions.
FAQs
To align how inspectors interpret GMP requirements, assess quality systems, and classify findings consistently across international pharmaceutical operations.
Because documentation quality, data integrity controls, and CAPA effectiveness are interpreted differently across inspections, even when manufacturing processes remain unchanged.
By strengthening traceability, timely GMP documentation, audit trail review, and CAPA effectiveness within core pharmaceutical quality systems.

Mahtab Shardi
Mahtab is a pharmaceutical professional with a Master’s degree in Physical Chemistry and over five years of experience in laboratory and QC roles. Mahtab contributes reliable, well-structured pharmaceutical content to Pharmuni, helping turn complex scientific topics into clear, practical insights for industry professionals and students.

Master GxP Validation in 2026: Meaning, Key Steps, and Validated State Control
Auditors want evidence you can trace, not opinions you can explain. GxP validation links intended use, requirements, risk, and test results into one story. When you control changes and review performance, you keep the system inspection-ready every day on time.

Master GMP Compliance in 2026: Meaning, Core Elements, and How to Implement
GMP compliance keeps medicines safe, consistent, and traceable across every batch. This guide explains core GMP elements, practical rollout steps, and common pitfalls. It also shows how to strengthen training, documentation, data integrity, and audit readiness.

History of Pharmacovigilance: From the Thalidomide Crisis (1961–2026) to GMP Oversight
Thalidomide in 1961 changed drug safety forever. Since then, pharmacovigilance has grown from crisis response to proactive risk management. Today, teams track signals, tighten reporting rules, and connect safety data to quality systems. As a result, PV now links directly to GMP oversight, audits, and data integrity.


