Pharmaceutical Documentation is cited in more than 60% of GMP inspection observations globally, with regulators consistently identifying documentation gaps as a primary driver of repeat findings and delayed inspection closeouts. In recent inspection cycles, agencies have emphasized that incomplete records, weak traceability, and late entries pose the same compliance risk as technical process failures. In practice, documentation is no longer treated as administrative paperwork but as regulatory evidence of control.
For QA/QC professionals, regulatory staff, and manufacturing leaders, GMP documentation systems sit at the center of regulatory enforcement. Inspectors rely on records to reconstruct manufacturing decisions, verify data integrity documentation, and confirm accountability across quality systems. This article explains how inspection-ready documentation functions as regulatory evidence, how it supports Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), and what regulators expect to see when assessing inspection readiness in real operating environments.
Table of Contents
What Is Pharmaceutical Documentation in a GMP Environment
Pharmaceutical documentation is regulated evidence showing that manufacturing and quality decisions were executed under control.
In a GMP context, GMP documentation systems represent the formal record of how processes were designed, executed, reviewed, and corrected. They capture not only what happened, but who performed the activity, when it occurred, and whether it met predefined requirements.
In simple terms:
Inspection-ready documentation proves that products were manufactured safely, consistently, and in line with approved procedures.
From an inspection perspective, data integrity documentation replaces assumptions with evidence. Regulators evaluate whether records demonstrate traceability, contemporaneous recording, and accountability across manufacturing and quality functions. When controlled documents in pharma are weak, inspectors cannot confirm control—even if the physical process appears compliant.
Why Pharma Documentation Is Critical for GMP Compliance
Inspectors use documentation to verify control, not to review paperwork. GMP enforcement relies on the principle that processes must be demonstrably controlled. Inspectors do not observe every batch or test; instead, they review records to reconstruct events and decisions. Documentation allows regulators to confirm that procedures were followed, deviations were investigated, and corrective actions were implemented effectively.
Well-controlled documentation enables inspectors to assess consistency over time. Poor documentation, by contrast, raises immediate questions about data integrity, training effectiveness, and management oversight. This is why documentation-related observations frequently escalate into broader compliance concerns during inspections.
Core Types of Documentation in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Inspectors review documentation to determine whether manufacturing and quality activities are executed, investigated, and controlled consistently across the product lifecycle. Rather than assessing records individually, regulators use documentation to verify traceability, data integrity, and accountability within GMP systems.
To assess inspection readiness, agencies focus on a defined set of documentation types that provide direct evidence of control:
- SOPs and Controlled Procedures
- Batch Manufacturing and Packaging Records
- Deviation, OOS, and CAPA Documentation
- Validation and Qualification Documentation
SOPs and Controlled Procedures
Standard Operating Procedures define how tasks must be performed and serve as the reference point for all GMP activities. Controlled SOP management ensures that only current, approved procedures are in use and that changes are documented, reviewed, and implemented consistently.
During inspections, regulators compare SOP content against observed practice. Gaps between written procedures and execution frequently trigger findings, particularly when outdated or uncontrolled documents remain in circulation.
Batch Manufacturing and Packaging Records
Batch records provide contemporaneous evidence that each manufacturing step was performed according to approved instructions. They capture critical parameters, operator actions, and in-process controls.
Inspectors scrutinize batch records for completeness, accuracy, and timing. Late entries, missing signatures, or unexplained corrections are often interpreted as data integrity risks rather than clerical errors.
Deviation, OOS, and CAPA Documentation
Deviation and investigation records demonstrate how quality issues are identified, assessed, and resolved. Regulators evaluate whether root causes are scientifically justified and whether corrective actions address systemic issues.
In practice, inspections frequently uncover investigations that close without sufficient evidence, lack trend analysis, or fail to link CAPAs to effectiveness checks—signaling weak quality decision-making.
Validation and Qualification Documentation
Validation records confirm that processes, equipment, and analytical methods operate as intended. Qualification documentation supports the reliability of systems used to generate GMP data.
Inspectors expect validation to be lifecycle-based, with documented rationale, acceptance criteria, and ongoing monitoring. Static or outdated validation packages often result in observations related to process reliability.
Data Integrity and Documentation Expectations
Data integrity principles commonly summarized through ALCOA+ require that records are attributable, legible, contemporaneous, original, accurate, complete, consistent, enduring, and available. Documentation practices operationalize these principles within GMP systems.
Inspectors assess whether records are created at the time of activity, whether audit trails are reviewed, and whether changes are transparent and justified. Weak documentation controls often lead to broader conclusions about cultural gaps in quality systems.
Common GMP Documentation Gaps Identified During Inspections
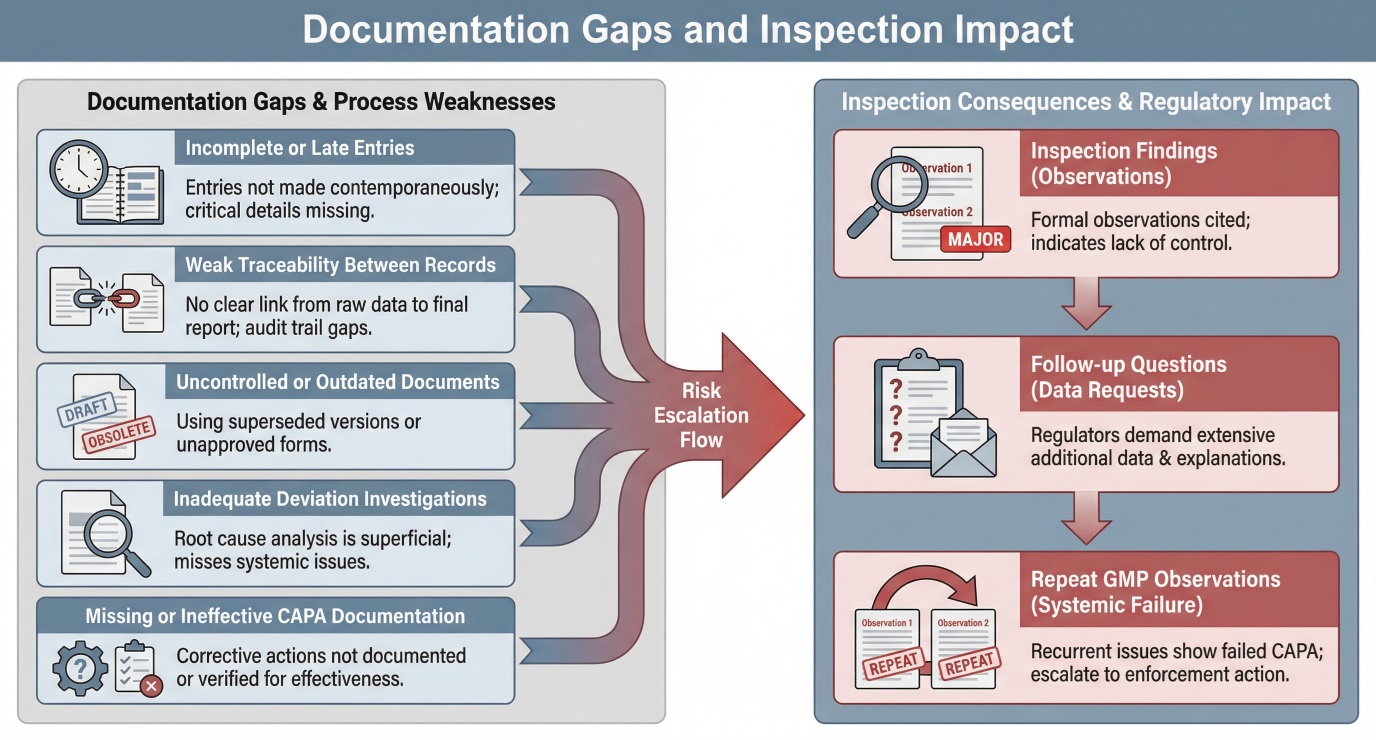
Regulatory findings frequently cite recurring documentation deficiencies, including:
- Incomplete or missing batch and test records
- Late or backdated entries without justification
- Weak document control and version management
- Inadequate traceability between deviations, investigations, and CAPAs
- Insufficient audit trail review and data governance
These gaps typically reflect systemic weaknesses rather than isolated errors. Inspectors expect organizations to identify patterns, not just correct individual records.
How Pharmaceutical Documentation Supports Inspection Readiness
Controlled documentation reduces inspection friction and follow-up questions.
When documentation is complete, controlled, and traceable, it allows inspectors to confirm process control quickly and with fewer follow-up questions.
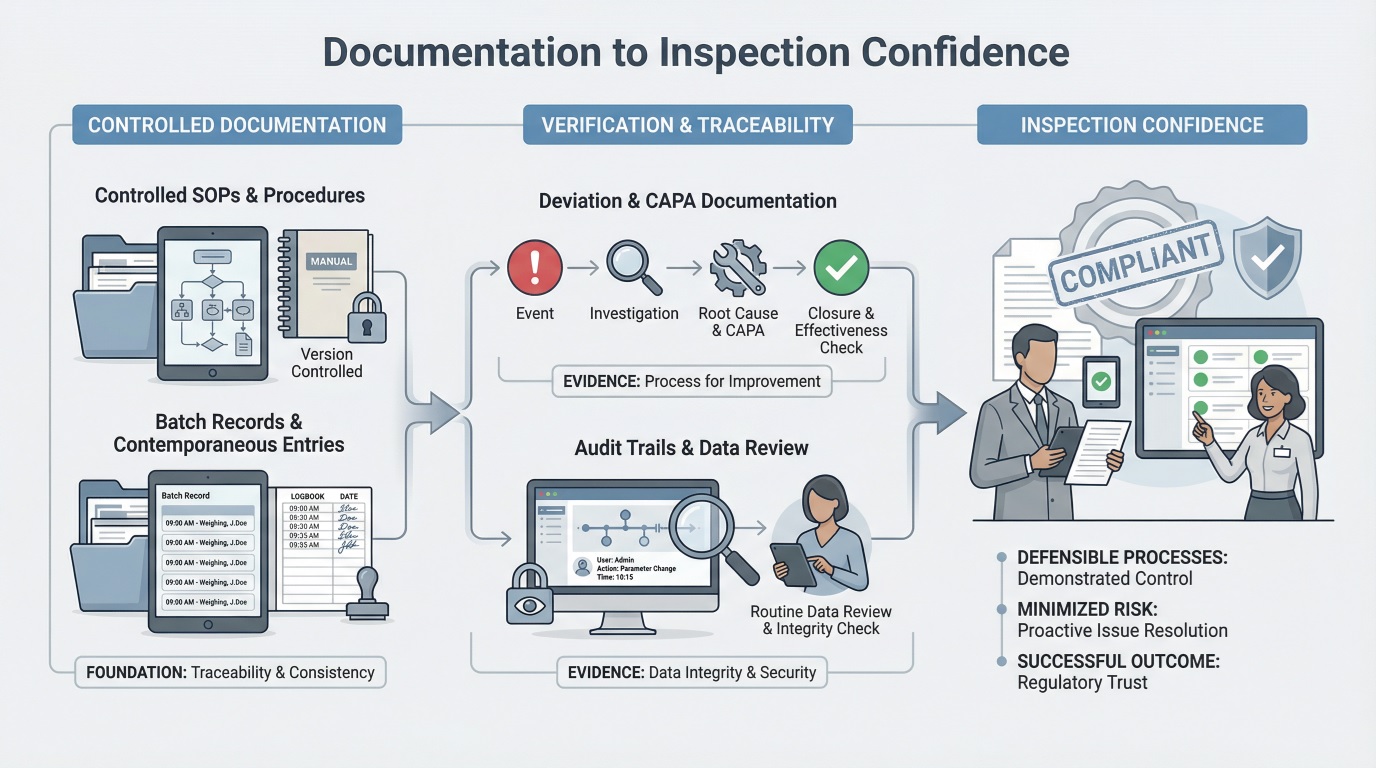
Inspection-ready documentation enables inspectors to quickly verify compliance without extensive clarification requests. Clear, traceable records demonstrate that quality systems function consistently under routine operating conditions.
Organizations with strong documentation practices experience fewer repeat observations, faster inspection closeouts, and reduced regulatory scrutiny. Documentation that aligns execution with oversight allows inspections to focus on confirmation rather than investigation.
Final Word
Recent GMP inspection analyses show that documentation and data integrity issues account for 10–15% of cited deficiencies, making them one of the most persistent causes of repeat GMP observations rather than isolated findings. These issues most often stem from incomplete records, weak traceability, late entries, and insufficient linkage between investigations and corrective actions areas that directly limit an inspector’s ability to confirm process control.
In practice, pharmaceutical documentation functions as a continuous risk-control system. It requires organizations to demonstrate control during routine operations, not reconstruct evidence under inspection pressure. Inspection outcomes increasingly depend on whether batch records, deviation files, and audit trails remain reliable when workload, complexity, and time constraints are highest where most compliance failures actually emerge.
FAQs
Batch manufacturing records, deviation investigations, and training records are typically reviewed first because they show real execution, traceability, and accountability under GMP conditions.
Because incomplete or late records prevent inspectors from confirming process control and data integrity, even when manufacturing equipment and facilities appear compliant.
Contemporaneous recording supported by controlled SOPs, audit trail review, and documented CAPA effectiveness consistently reduces inspection questions and follow-up actions.
References

Mahtab Shardi
Mahtab is a pharmaceutical professional with a Master’s degree in Physical Chemistry and over five years of experience in laboratory and QC roles. Mahtab contributes reliable, well-structured pharmaceutical content to Pharmuni, helping turn complex scientific topics into clear, practical insights for industry professionals and students.

Sampling Plan in Pharma: GMP, FDA/EMA Expectations, and QC Workflow
A pharmaceutical sampling plan ensures that tested samples truly represent the entire batch. Because results determine product release, regulators require representative collection, justified sample size, controlled handling, and full documentation. Strong sampling practices reduce risk, support compliance, and protect patient safety.

Pharma Jobs in Qatar in 2026: Employers, Licensing, and Market Demand
Qatar’s pharmaceutical sector continues to evolve through hospital expansion, regulatory oversight, and structured workforce planning. This article explores pharmacy jobs in Qatar, key employer segments, licensing requirements, and the education pathways that shape long-term career opportunities.

GMP Packaging in 2026: Requirements, Guidelines, Controls, and Primary vs Secondary Packaging
GMP packaging protects product identity, quality, and traceability while preventing mix-ups and labeling errors. Strong controls such as line clearance, reconciliation, and component management ensure only correct, compliant products reach patients and markets.