More than 70% of major regulatory safety actions worldwide take place after a medicine receives approval, according to global safety surveillance data. This figure highlights a critical reality: drug safety does not end at market authorization. Instead, it evolves as medicines reach broader patient populations.
Global safety authorities rely on lifecycle oversight to identify risk patterns that emerge after widespread use begins. For this reason, pharmacovigilance phases exist as a structured framework that supports long-term patient protection across a product’s lifespan.
Rather than isolated checkpoints, these phases form a connected system governing how safety data are collected and evaluated throughout development.
In this article, we explain lifecycle-based safety oversight as a continuous process, from early development through post-marketing safety monitoring.
Learn more about the fundamentals of pharmacovigilance and its regulatory role.
Table of Contents
What Are Pharmacovigilance Phases
Pharmacovigilance phases describe the sequential stages of safety oversight applied throughout a medicinal product’s lifecycle. Regulatory authorities require this approach because safety knowledge expands over time.
Early development involves limited exposure under controlled conditions. After approval, medicines interact with real-world variables such as longer use and combination therapies. Therefore, safety monitoring must remain adaptive.
These phases typically include:
- Early development safety
- Safety oversight during clinical trials
- Pre-approval benefit–risk evaluation
- Post-marketing pharmacovigilance
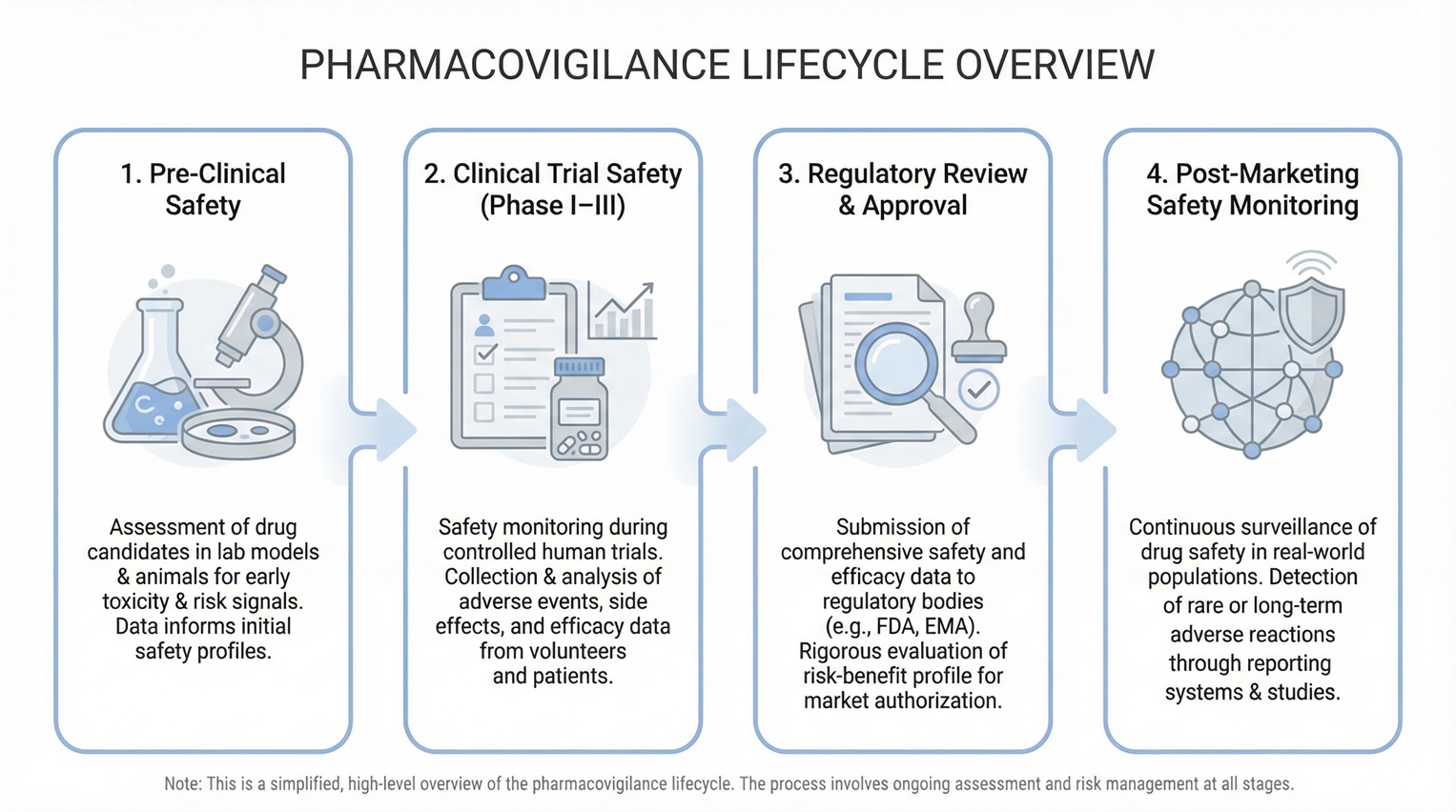
Phase One: Pre-Clinical and Early Development Safety
The first pharmacovigilance phase begins before human exposure. During non-clinical development, researchers identify initial safety signals and potential risk factors.
Toxicology studies, pharmacology data, and dose-ranging experiments establish early safety assumptions. These findings guide first-in-human study designs and monitoring priorities.
As early clinical data emerge, teams reassess these assumptions. Consequently, early development safety sets the foundation for later pharmacovigilance activities.
Phase Two: Pharmacovigilance During Clinical Trials
During Phase 1 to Phase 3 trials, pharmacovigilance becomes operational and continuous. Sponsors actively monitor participant safety, while regulators maintain close oversight.
Key clinical-phase safety activities include:
- Continuous adverse event reporting
- Ongoing medical review of safety data
- Periodic safety analyses and listings
- Independent safety committee oversight
- Timely regulatory safety submissions
At this stage, clinical trial safety focuses on early detection and structured evaluation. Teams review safety findings cumulatively across studies.
While clinical trials generate controlled safety evidence, regulators ultimately require a broader, integrated view of risk before approval—one that connects trial data with real-world expectations.
Phase Three: Transition From Clinical Development to Market
This transition phase represents a decisive regulatory milestone. Accumulated safety data must now support a favorable benefit–risk assessment.
Regulators evaluate whether identified risks remain acceptable under proposed conditions of use. At the same time, organizations must demonstrate readiness for ongoing pharmacovigilance after approval.
In practice, safety gaps often emerge when documented processes fail to align with operational reality. Therefore, this phase plays a critical role in translating development data into sustainable safety systems after approval.
We will discuss:
- Adverse Event Collection and Reporting
- Signal Detection and Risk Evaluation
- Risk Management Planning
- Regulatory Review and Safety Commitments
- Data Integration Across Development Phases
Adverse Event Collection and Reporting
Adverse event handling remains central across the entire product lifecycle. However, regulatory expectations intensify as products approach approval.
Core expectations include:
- Timely intake and assessment of cases
- Accurate seriousness and causality evaluation
- Consistent safety database documentation
- Compliance with reporting timelines
Meeting these requirements demonstrates system robustness and inspection readiness.
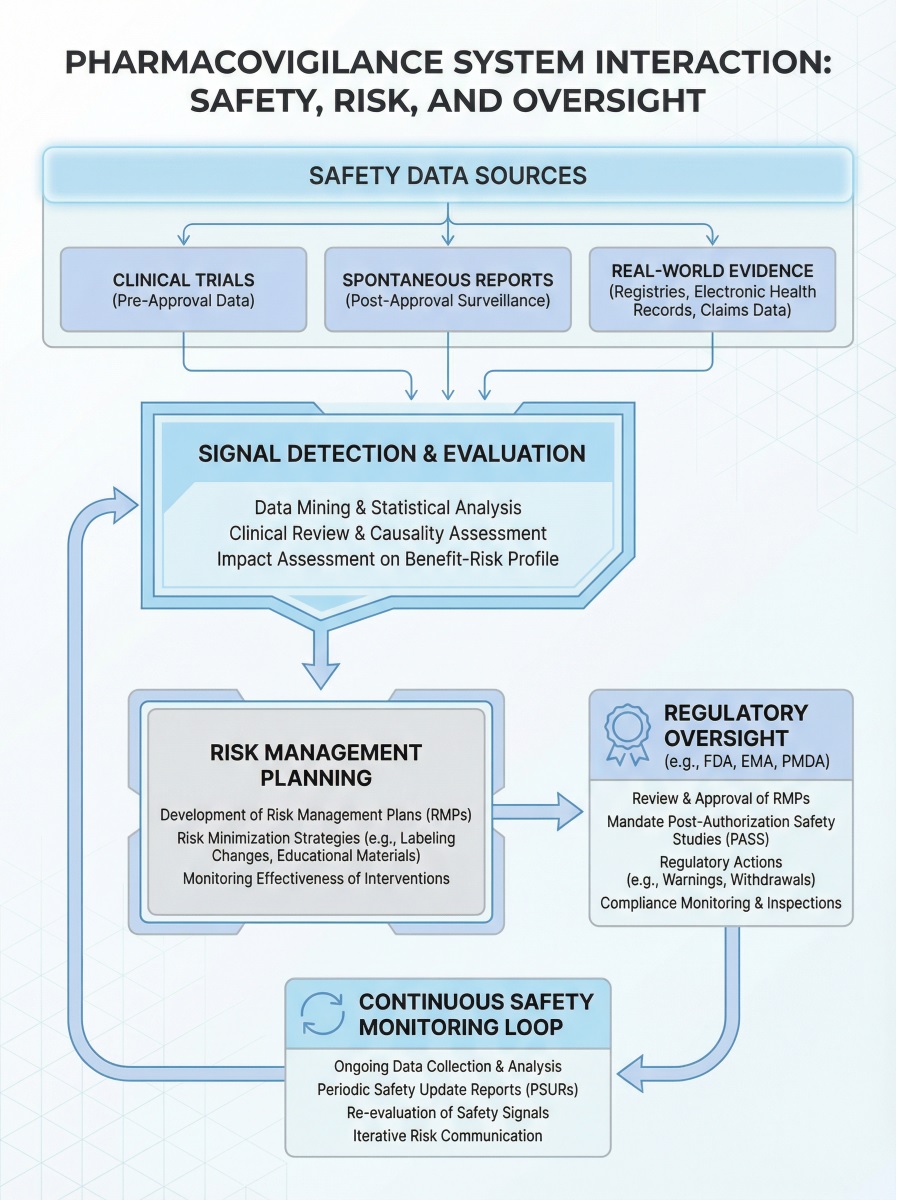
Signal Detection and Risk Evaluation
Signal detection identifies emerging safety concerns across datasets. Teams combine medical review, trend analysis, and statistical methods to evaluate potential risks.
Importantly, signal evaluation integrates data from multiple studies and sources. This approach strengthens risk interpretation and supports regulatory decision-making.
Risk Management Planning
A risk management plan defines how organizations will monitor and minimize risks after approval. Regulators expect these plans to reflect real, evidence-based concerns.
Effective plans outline:
- Identified and potential risks
- Pharmacovigilance activities
- Risk minimization measures
- Post-authorization commitments
Risk management planning links development data with real-world safety responsibilities.
Regulatory Review and Safety Commitments
Before approval, authorities assess both safety evidence and pharmacovigilance systems. They confirm whether organizations can manage risks proactively.
As a result, regulators may impose post-approval obligations such as enhanced monitoring or additional studies. These commitments extend safety responsibilities beyond market entry.
Data Integration Across Development Phases
Strong pharmacovigilance systems ensure seamless data flow across phases. Early signals inform later decisions, while cumulative analyses refine benefit–risk understanding.
Without integration, safety oversight becomes fragmented. Lifecycle-based pharmacovigilance depends on continuity and traceability.
Post-Marketing Pharmacovigilance Phases and Real-World Safety Monitoring
After approval, safety monitoring expands significantly. Real-world use introduces variability that clinical trials cannot fully capture.
Regulatory data show that fewer than 20% of serious safety risks are fully identified before approval, while most emerge during routine clinical use. As a result, post-marketing pharmacovigilance plays a decisive role in long-term patient protection.
Key post-marketing activities include:
- Spontaneous adverse event reporting
- Periodic safety update reporting
- Signal detection using real-world data
- Benefit–risk reassessment
- Evaluation of risk minimization effectiveness
Through structured monitoring, rare and delayed adverse drug reactions become detectable.
Why Understanding Lifecycle Safety Oversight Matters
Understanding lifecycle safety oversight improves compliance, inspection readiness, and system design as products move into real-world use. It helps teams manage safety risks more consistently across development and post-approval stages. Ultimately, it supports safer therapies for patients
Final Words
Global safety databases process over 2,000,000 adverse event reports each year, yet many of the most impactful safety actions only emerge after patterns repeat in real-world use. This highlights a key reality: effective safety decisions rarely depend on a single study or moment.
Pharmacovigilance phases connect early development data with post-marketing evidence, allowing risks to be reassessed and managed over time. When safety oversight follows a lifecycle approach, responses become proactive rather than reactive.
For professionals working with medicinal products, this understanding strengthens inspection readiness, supports better decisions, and ultimately contributes to safer therapies for patients.
FAQs
Clinical trial phases focus on controlled development milestones such as dose selection and efficacy assessment. Lifecycle safety monitoring extends beyond trials to continuously evaluate safety risks during routine clinical use.
Formal safety monitoring begins with first-in-human studies, when adverse event collection becomes systematic. However, safety planning starts earlier during non-clinical development, where toxicology and pharmacology data shape initial risk assumptions for later phases.
Clinical trials involve selected populations and limited exposure. Once products reach routine use, broader patient groups, longer treatment durations, and real-world conditions can reveal rare or delayed adverse reactions not seen during development.
Risk management plans translate safety data into structured post-approval actions. They define how risks are monitored, minimized, and reassessed over time, ensuring alignment with real-world evidence and evolving benefit–risk evaluations.
References

Ershad Moradi
Ershad Moradi, a Content Marketing Specialist at Zamann Pharma Support, brings 6 years of experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Specializing in pharmaceutical and medical technologies, Ershad is currently focused on expanding his knowledge in marketing and improving communication in the field. Outside of work, Ershad enjoys reading and attending industry related networks to stay up-to-date on the latest advancements. With a passion for continuous learning and growth, Ershad is always looking for new opportunities to enhance his skills and contribute to pharmaceutical industry. Connect with Ershad on Facebook for more information.

Master GxP Validation in 2026: Meaning, Key Steps, and Validated State Control
Auditors want evidence you can trace, not opinions you can explain. GxP validation links intended use, requirements, risk, and test results into one story. When you control changes and review performance, you keep the system inspection-ready every day on time.

Master GMP Compliance in 2026: Meaning, Core Elements, and How to Implement
GMP compliance keeps medicines safe, consistent, and traceable across every batch. This guide explains core GMP elements, practical rollout steps, and common pitfalls. It also shows how to strengthen training, documentation, data integrity, and audit readiness.

History of Pharmacovigilance: From the Thalidomide Crisis (1961–2026) to GMP Oversight
Thalidomide in 1961 changed drug safety forever. Since then, pharmacovigilance has grown from crisis response to proactive risk management. Today, teams track signals, tighten reporting rules, and connect safety data to quality systems. As a result, PV now links directly to GMP oversight, audits, and data integrity.


