Pharmaceutical safety grows fast and complex. Global medicine sales already pass USD 1.5 trillion, and thousands of new products move through pipelines every year. Therefore, companies need clear, harmonised rules that protect patients in every region. The ICH guidelines for pharmacovigilance give this structure across the full product lifecycle.
Today, more than 20 regulators and industry members work within ICH, and over 80 countries follow or reference its standards. These rules guide safety teams from Phase I–III clinical trials to Phase IV post-marketing and help manage millions of ICSRs each year. For a stronger foundation, you can study core concepts of pharmacovigilance at during your learning journey.
Table of Contents
What Are ICH Guidelines for Pharmacovigilance?
The International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) created these guidelines. ICH brings together regulators and industry experts from the EU, US, Japan, and other regions. Together, they design global standards that simplify drug development and safety reporting.
The ICH pharmacovigilance requirements focus on how companies collect, evaluate, and report safety data. They help teams manage patient risks and ensure consistent formats across regulatory regions. Additionally, the guidelines protect public health because they support transparent communication about safety events and product risks.
Where Pharmacovigilance Guidelines from ICH Should Apply?
Companies apply these guidelines during clinical trials and post-marketing phases. They cover any activity that involves monitoring, detecting, assessing, and reporting adverse events. Therefore, they apply to:
Sponsors running clinical studies
MAHs (Marketing Authorisation Holders)
Contract Research Organisations (CROs)
Global safety teams that manage ICSRs
Any region that accepts ICH harmonisation, including Europe, the US, Japan, and many additional authorities
Because ICH aims to unify global expectations, many non-ICH countries also follow these rules.
Key ICH guidelines (Requirements) for Pharmacovigilance
Which are the ICH guidelines for pharmacovigilance? Below is the essential E2 series:
E2A – Clinical Safety Data Management: Definitions and Standards for Expedited Reporting
E2B(R2) and E2B(R3) – Electronic Transmission of ICSRs
E2C (now E2C(R2) / PBRER) – Periodic Benefit-Risk Evaluation Reports
E2D – Post-approval Safety Data Management: Expedited Reporting
E2E – Pharmacovigilance Planning
E2F – Development Safety Update Reports (DSURs)
Each document defines how safety teams should identify, process, and share safety information.
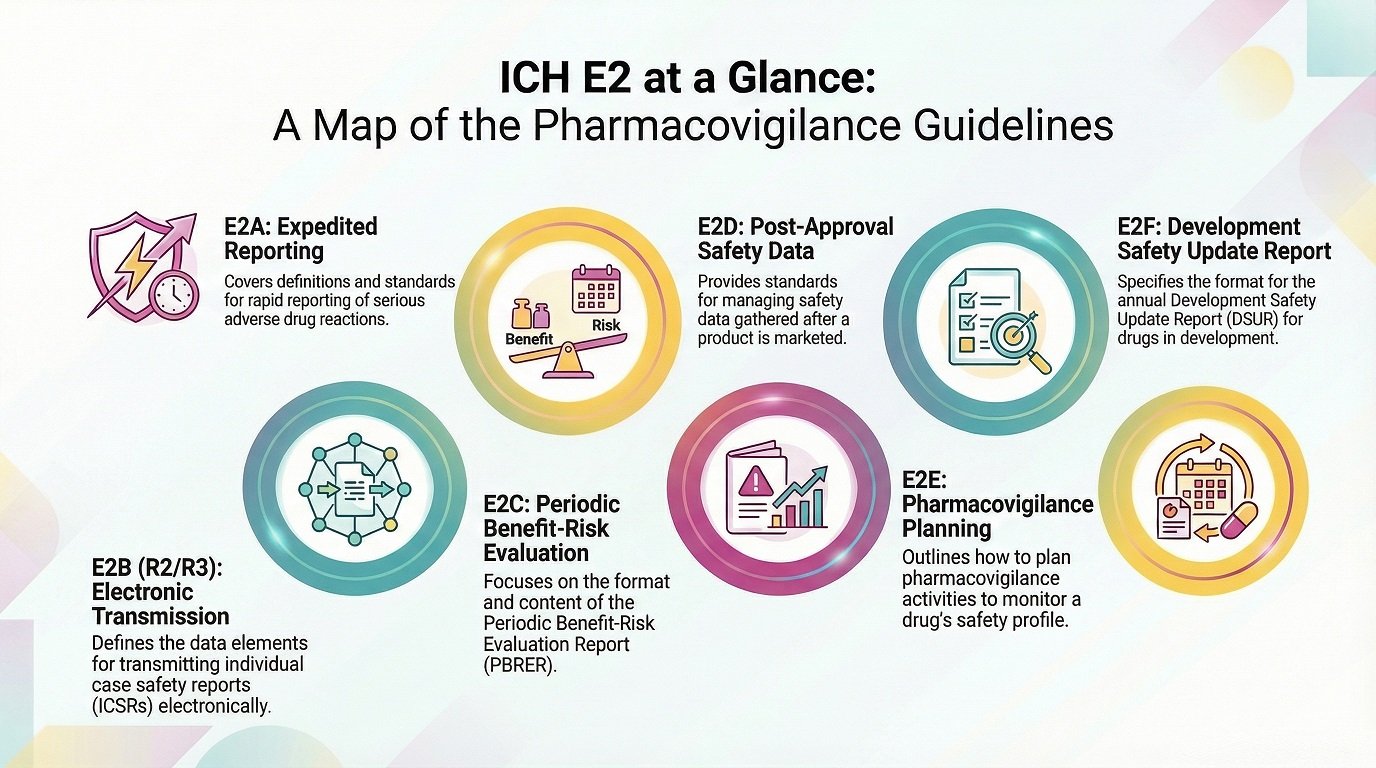
E2A – Clinical Safety Data Management: Definitions and Standards for Expedited Reporting
E2A defines core terminology and explains how companies must evaluate serious and unexpected adverse events. It also defines timelines for expedited reporting during clinical development.
E2B(R2) and E2B(R3) – Electronic Transmission of Individual Case Safety Reports (ICSRs)
These guidelines define the electronic structure of ICSRs. They establish data fields, message formats, and how companies transmit reports to regulators. Today, E2B(R3) supports advanced digital safety systems across the globe.
E2C – Periodic Safety Update Reports (PSUR) / PBRER
E2C (now revised as E2C(R2)) explains how companies prepare long-term benefit-risk evaluation reports. Regulators use these documents to assess emerging risks after approval.
E2D – Post-approval Safety Data Management: Expedited Reporting
E2D clarifies how marketing authorisation holders submit expedited post-marketing reports. It also aligns global timelines for serious and unexpected adverse reactions.
ICH PV Guidelines to Regional Rules
Global teams follow ICH as the base. However, regulators add regional requirements. Europe uses GVP Modules. The US relies on FDA CFR Parts 312 and 314. Japan and Canada add extra timelines and submission formats.
Because safety systems differ, companies build global SOPs that map ICH expectations to regional rules. This approach allows safety teams to operate consistently while still meeting local requirements. It also reduces compliance risks, especially when handling complex ICSRs.
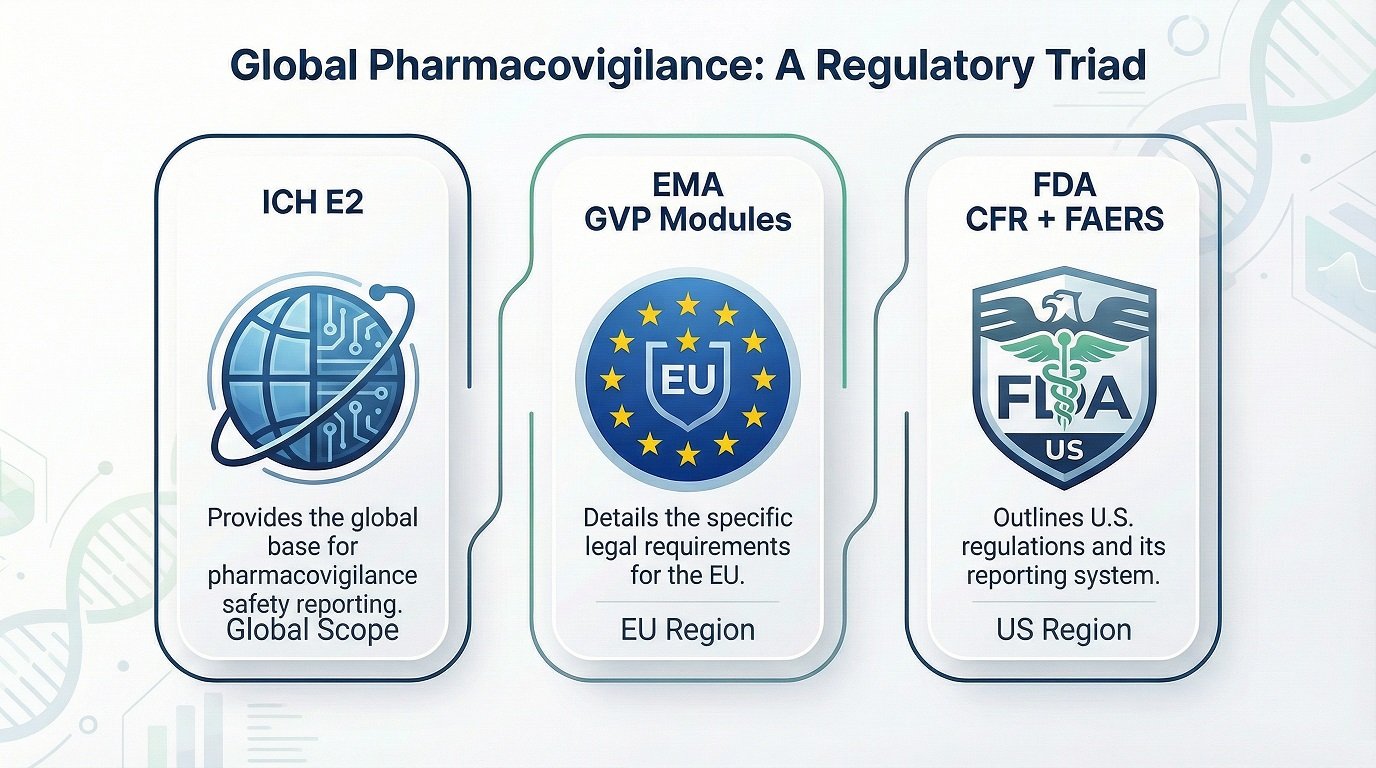
Link Between ICH E2 and FDA Safety Requirements
FDA aligns strongly with ICH E2 guidelines. However, FDA adds specific timelines and submission rules. For example:
FDA receives safety reports via FAERS
FDA requires 15-day expedited reports for serious, unexpected events
FDA inspections check compliance with both ICH and CFR rules
Additionally, FDA encourages structured electronic submissions that follow E2B(R3). Many companies streamline workflows because this alignment reduces manual reporting work.
Final words
The ICH guidelines for pharmacovigilance standardize global safety work. They define how teams handle ICSRs, expedited reports, and benefit–risk evaluations through the E2A–E2F series. As a result, companies manage data consistently from first-in-human studies to 10–20 years of post-marketing use.
When you understand these rules, you reduce reporting errors and meet strict 15-day timelines more easily. At the same time, growing case volumes in the millions create strong demand for skilled PV staff. You can plan your next steps with the pharmacovigilance career path at and move toward higher-responsibility roles in drug safety.
FAQs
The key E2 guidelines include E2A, E2B(R2/R3), E2C(R2), E2D, E2E, and E2F. E2A and E2D guide expedited reporting. E2B defines electronic case formats. E2C covers periodic benefit–risk reports. E2E and E2F support pharmacovigilance planning and development safety updates.
ICH E2 sets the global base, while EMA GVP and FDA regulations add regional details such as timelines, formats, and system requirements.
Yes, many non-ICH authorities adopt or reference ICH E2 because it simplifies global development, supports inspections, and improves data quality.
References

Ershad Moradi, a Content Marketing Specialist at Zamann Pharma Support, brings 6 years of experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Specializing in pharmaceutical and medical technologies, Ershad is currently focused on expanding his knowledge in marketing and improving communication in the field. Outside of work, Ershad enjoys reading and attending industry related networks to stay up-to-date on the latest advancements. With a passion for continuous learning and growth, Ershad is always looking for new opportunities to enhance his skills and contribute to pharmaceutical industry. Connect with Ershad on Facebook for more information.

WHO GMP in 2026: Inspection Readiness and Compliance Expectations
This article explains how global pharmaceutical GMP standards are applied during inspections, why operational gaps persist despite formal compliance, and how quality systems, contamination control, and risk-based execution shape regulatory inspection readiness across manufacturing operations.

Audit Observation in Pharma (2026 guide): Meaning, Types, and GMP Classification
Audit observations help pharma teams identify GMP gaps before they become bigger failures. When teams classify findings correctly, they prioritize CAPA actions faster, justify risk decisions clearly, and improve inspection readiness through stronger evidence, ownership, and effectiveness checks across operations.

GMP Environments in 2026: Inspection Readiness and Control Expectations
This article explains how inspectors evaluate GMP environments during regulatory inspections, why environmental findings often repeat, and how facility design, flow control, monitoring, and risk-based controls shape inspection readiness in real pharmaceutical manufacturing operations.


