In recent regulatory inspections, documentation failures continue to rank among the most frequent GMP compliance issues. Based on FDA inspection trend analyses, over 50% of Form 483 observations issued annually include at least one finding related to documentation, recordkeeping, or data integrity. This statistic shows why documentation weaknesses remain a primary compliance risk under Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
In GMP environments, inspectors do not rely on explanations or intentions. Instead, they assess documented evidence. For this reason, strong GMP documentation – GDocP practices directly influence inspection outcomes, regulatory confidence, and patient safety.
Table of Contents
What Is GMP Documentation Under GDocP
Pharmaceutical records and documentation describe how products are manufactured, tested, released, and distributed. Within this framework, GMP documentation – GDocP defines how these records are created, controlled, and maintained to meet regulatory expectations.
Together, structured documentation controls ensure reliable, traceable, and inspection-ready data throughout the product lifecycle.
Purpose of GMP Documentation in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Documentation plays a central role in pharmaceutical quality systems. Most importantly, it enables organizations to:
- Demonstrate control over manufacturing and testing processes
- Prove alignment between approved procedures and executed activities
- Support data reliability and regulatory compliance
- Enable effective deviation investigation and CAPA management
- Provide objective evidence during inspections
Inspectors often view documentation quality as a reflection of organizational discipline and quality culture.
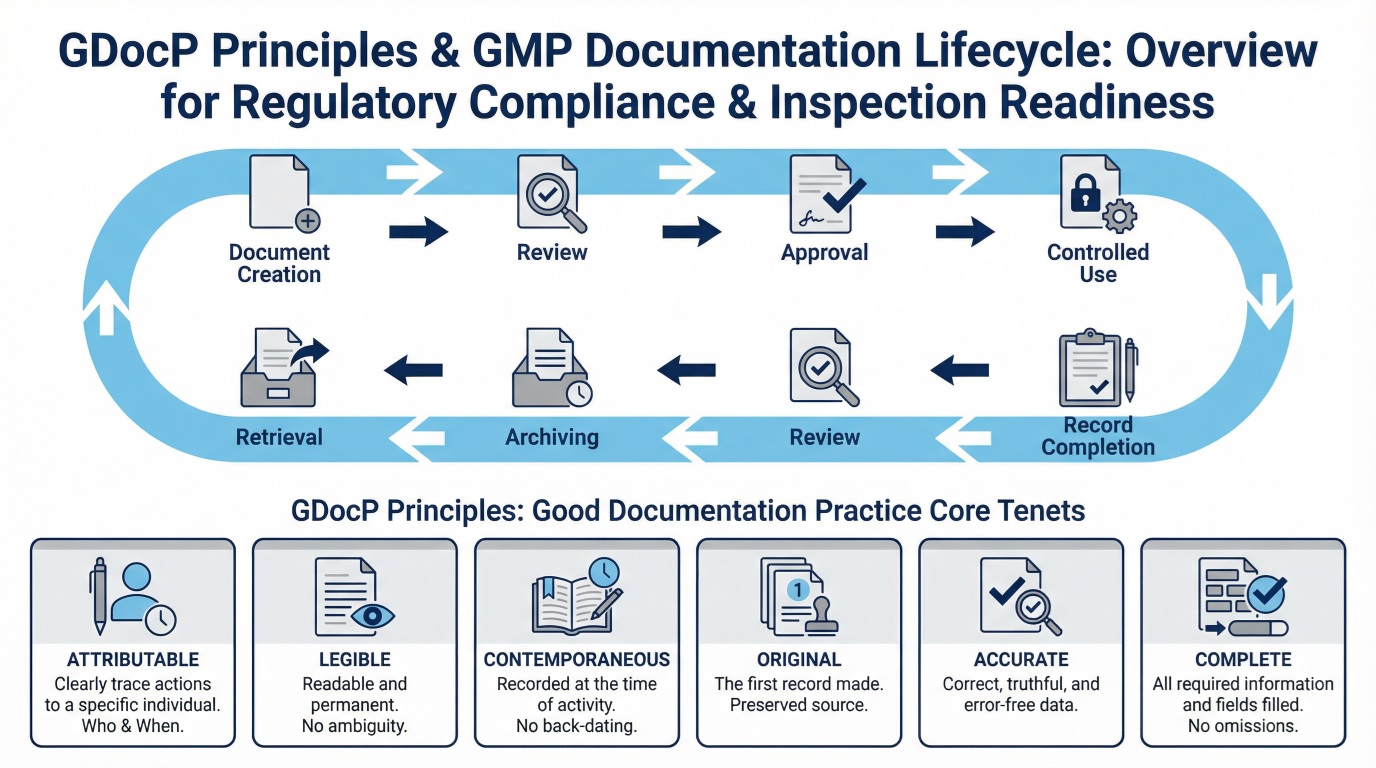
Core Documentation Principles Supporting Data Integrity
The core documentation principles align with data integrity concepts. These principles ensure that GMP records remain trustworthy and usable during inspections.
Key principles include:
- Attributable: Each entry clearly identifies who performed the activity
- Legible: Records remain readable throughout their retention period
- Contemporaneous: Personnel record data at the time of the activity
- Original: Records preserve original data or verified true copies
- Accurate: Entries reflect actual observations without distortion
When organizations consistently apply these principles, documentation becomes a reliable compliance tool rather than a regulatory burden.
Types of GMP Documents and Records
Pharmaceutical operations rely on multiple categories of GMP records to support quality systems and inspections. In practice, GMP documentation – GDocP sets clear expectations for how teams create, complete, and retain these records.
Production-related documents
- Master Batch Records (MBRs)
- Executed Batch Records (BMRs)
- Equipment logbooks
Quality Control documents
- Laboratory notebooks
- Analytical worksheets
- Stability and testing records
Quality Assurance documents
- SOPs and policies
- Deviation and CAPA records
- Change control documentation
Support and compliance records
- Training and competency files
- Validation and qualification reports
All these documents must follow formal document control processes to prevent unauthorized use.
We will discuss:
- Controlled Documents and Version Management
- Data Integrity and Documentation Accuracy
- Common Documentation Errors Identified During Inspections
- Review, Approval, and Archiving of GMP Records
- Documentation Traceability and Audit Readiness
Controlled Documents and Version Management
Controlled documents form the backbone of GMP systems. In this context, GMP documentation – GDocP defines clear expectations for document issuance, revision, and retirement to maintain traceability and inspection readiness.
Effective document control includes:
- Unique document identification and version numbers
- Defined review and approval workflows
- Controlled distribution of current versions
- Immediate withdrawal of obsolete documents
Without strong version management, inspectors may question data reliability and documentation traceability.
Data Integrity and Documentation Accuracy
Data integrity relies on accurate and transparent documentation practices. Every correction must remain visible and properly justified.
For example, when an operator records a weight incorrectly in a batch record, they should cross out the error with a single line, enter the correct value, and add initials, date, and a brief reason. This approach preserves original data while maintaining transparency.
Such practices demonstrate effective document control in GMP and consistent application of data integrity principles at the operational level.
Common Documentation Errors Identified During Inspections
During inspections, regulators frequently identify recurring documentation deficiencies, including:
- Backdated or pre-filled entries
- Missing signatures or dates
- Illegible handwriting
- Incomplete batch documentation
- Use of uncontrolled document copies
Although these issues may appear minor, inspectors often interpret them as indicators of systemic quality weaknesses.
Review, Approval, and Archiving of GMP Records
Effective management of GMP records and documentation requires timely review and formal approval by authorized personnel.In addition, companies must archive records securely to ensure long-term accessibility.
Regulatory expectations typically include:
- Defined review timelines
- Independent quality oversight
- Secure and retrievable storage systems
- Clearly defined retention periods
Strong archiving practices support both routine operations and inspections.
Documentation Traceability and Audit Readiness
Traceable documentation allows inspectors to follow the full history of a product, process, or deviation. As a result, traceability directly supports audit efficiency and regulatory trust. Well-structured documentation systems enable faster inspections and reduce compliance risk.
Therefore, inspection readiness depends on clear document traceability, defined documentation requirements, and consistent application of documentation standards across departments.
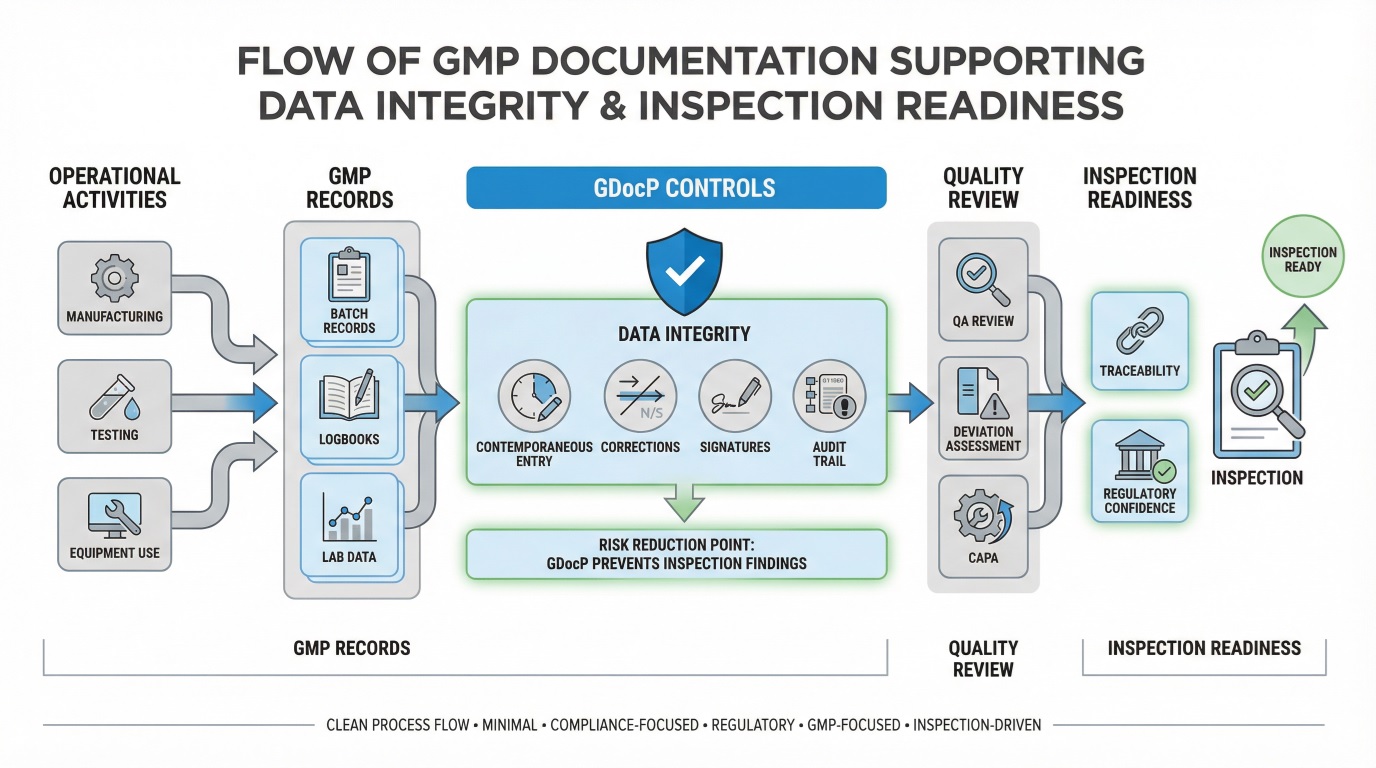
Documentation Expectations During Regulatory Inspections
Inspectors evaluate documentation content and behavior. They assess whether records accurately reflect actual operations and whether staff consistently follow approved documentation standards.
During inspections, regulators typically focus on:
- Completeness of batch records
- Consistency between SOPs and executed activities
- Data integrity safeguards
- Change control and deviation documentation
- Effectiveness of documentation training
Any inconsistency often triggers deeper system-level reviews.
Building an Inspection-Ready Documentation Framework
Organizations strengthen compliance by designing documentation systems that support daily operations, not only inspections.
Key elements include:
- Clear documentation hierarchies
- Robust document control workflows
- Regular training on documentation standards
- Periodic internal audits
- Continuous improvement mechanisms
When documentation reflects real operations, inspections become confirmation exercises rather than risk events.
Final Words
Quality records and documentation systems remain closely examined elements in every regulatory inspection.FDA Form 483 trend analyses consistently show that over 50% of inspection observations reference documentation, recordkeeping, or data integrity failures. This recurring pattern confirms that inspectors treat documentation as direct evidence of quality control, and in practice, GMP documentation – GDocP often serves as a primary indicator of inspection readiness.
Regulators assume undocumented activities did not occur. Consequently, weak documentation practices raise concerns about process control and patient safety, while inspection-ready systems signal compliance maturity and a strong quality culture.
FAQs
Batch records must allow an independent reviewer to fully reconstruct manufacturing and testing activities performed under GMP conditions. During batch release and inspection activities, regulators expect records to show clear timelines, complete entries, and contemporaneous documentation without reliance on verbal explanations.
During GMP inspections of regulated manufacturing sites, inspectors closely scrutinize unexplained corrections, missing signatures, inconsistent timestamps, and the use of uncontrolled documents. These issues often signal weaknesses in data integrity controls and quality oversight.
Within pharmaceutical quality systems, organizations should review controlled documents at defined intervals based on process criticality, regulatory expectations, and change history. Even in the absence of updates, periodic review demonstrates active document ownership.
References

Mahtab Shardi
Mahtab is a pharmaceutical professional with a Master’s degree in Physical Chemistry and over five years of experience in laboratory and QC roles. Mahtab contributes reliable, well-structured pharmaceutical content to Pharmuni, helping turn complex scientific topics into clear, practical insights for industry professionals and students.

GMP Environments in 2026: Inspection Readiness and Control Expectations
This article explains how inspectors evaluate GMP environments during regulatory inspections, why environmental findings often repeat, and how facility design, flow control, monitoring, and risk-based controls shape inspection readiness in real pharmaceutical manufacturing operations.

Adverse Event Reporting in 2026: Meaning, FAERS, EudraVigilance, And A Step-By-Step Guide
Adverse event reporting helps patients, healthcare professionals, and companies share safety concerns fast. Use the correct portal, submit complete case details, and send follow-up information. Clear reports support signal detection, risk review, and better pharmacovigilance decisions across systems globally today.

Master GxP Validation in 2026: Meaning, Key Steps, and Validated State Control
Auditors want evidence you can trace, not opinions you can explain. GxP validation links intended use, requirements, risk, and test results into one story. When you control changes and review performance, you keep the system inspection-ready every day on time.


