The pharmaceutical industry is constantly evolving with the introduction of new technologies, standards, and regulations. Regulatory agencies play a crucial role in ensuring that pharmaceutical products meet safety, quality, and efficacy standards.
In the rapidly changing landscape of global health and medicine, these regulatory bodies frequently update their guidelines. Staying informed on the latest regulatory agency updates is critical for pharmaceutical professionals who aim to remain compliant and competitive.
In this article, we will explore the latest updates and their impact on the pharma industry.
What Is a Regulatory Agency and Why Is It Crucial in Pharma?
A regulatory agency is a governmental body responsible for regulating specific industries, including the pharmaceutical sector. These agencies ensure that pharmaceutical companies adhere to strict guidelines for the production, testing, and marketing of drugs and medical devices. They oversee drug approvals, clinical trials, labeling, and post-market surveillance. With public health and safety as their primary concern, these agencies provide a framework for ensuring pharmaceutical products meet necessary standards before reaching consumers.
In the pharma industry, the regulatory agency serves as the gatekeeper. Their role involves monitoring drug efficacy, safety, and adherence to national and international standards. Agencies such as the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration), the EMA (European Medicines Agency), and the WHO (World Health Organization) work across borders, ensuring that pharmaceutical practices are uniform and reliable. The process of obtaining regulatory approval can be lengthy and complex, but it guarantees the safety and effectiveness of treatments, ultimately protecting public health.
Sign up for Introduction to GMP Quality Management Systems Course
Key Regulatory Agency Bodies in the Pharma Industry
These agencies not only enforce compliance but also issue updated guidelines regularly to keep pace with technological advances and global health challenges.
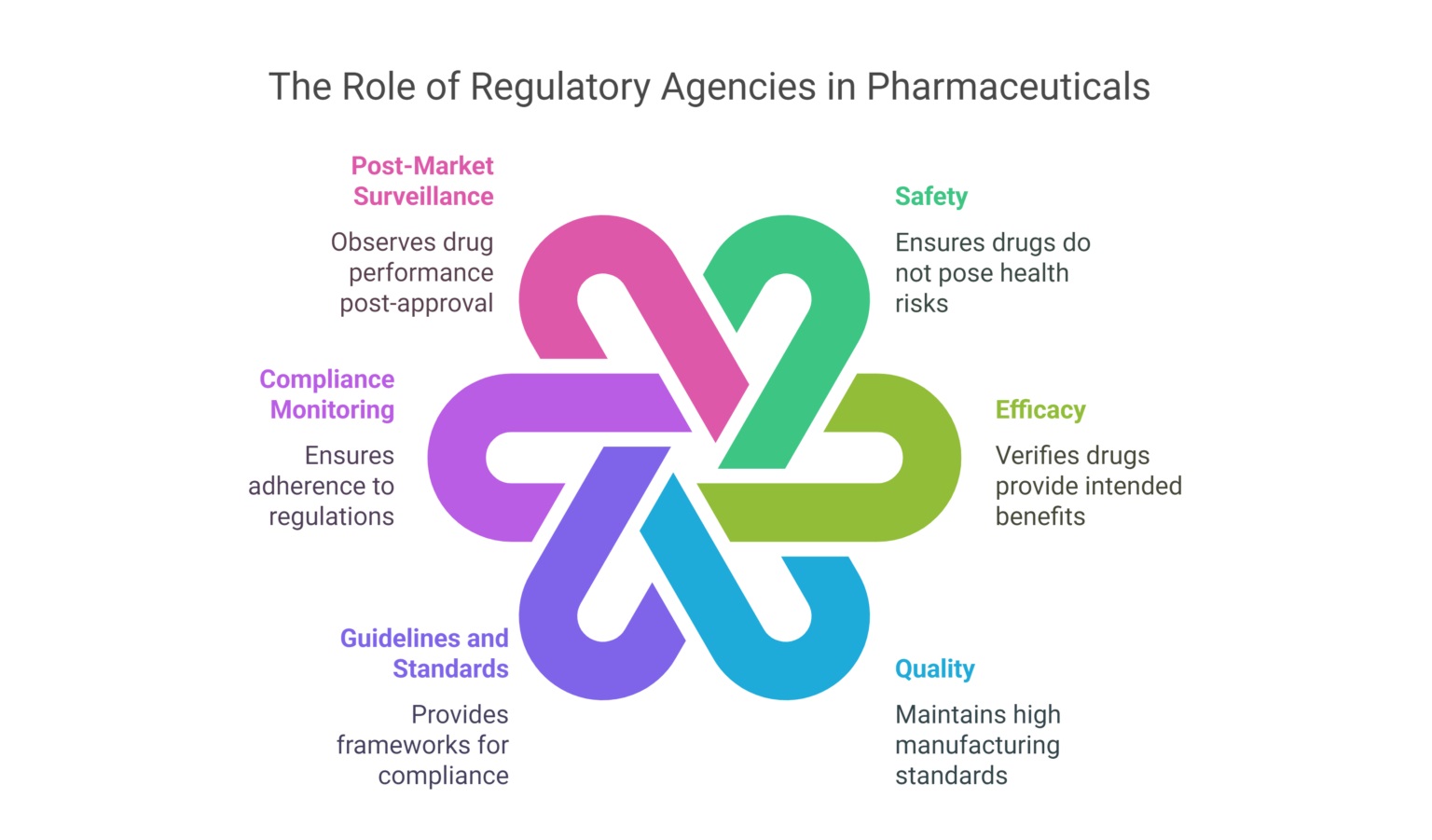
7 Main Objectives of a Regulatory Agency in Pharma
Regulatory agencies have a set of key objectives that directly impact the pharmaceutical industry. These objectives ensure that drug development, manufacturing, and distribution meet high safety and quality standards. Below are the main objectives:
Regulatory agencies are tasked with ensuring that only safe and effective drugs are available for patients. This is their highest priority.
Agencies aim to protect public health by regulating the manufacturing, labeling, and distribution of pharmaceutical products.
Encouraging innovation while ensuring safety is crucial. Regulatory bodies help expedite approvals for breakthrough therapies.
Regulatory bodies verify that drugs provide the intended benefits and have scientifically backed efficacy claims.
After a drug hits the market, agencies continuously monitor its performance and ensure that any adverse effects are addressed quickly.
Regulatory agencies enforce compliance with good manufacturing practices (GMP), clinical trial standards, and labeling guidelines.
These agencies work toward international standardization to ensure that drugs are universally safe and effective across different regions.
How Each Regulatory Agency Compares: FDA vs. EMA vs. WHO
FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration)
The FDA is a U.S. regulatory agency that sets the standard for drug approvals. It ensures drugs meet high safety and efficacy standards before they reach the market.
The agency follows a rigorous approval process, often requiring extensive clinical trial data. This process helps verify that drugs are both effective and safe for public use. The FDA’s thorough evaluation ensures patients receive quality treatments with minimal risks.
In addition to its standard procedures, the FDA offers fast-tracking programs. For example, Breakthrough Therapy Designation speeds up approval for drugs addressing serious unmet needs.
These programs allow drugs to reach the market faster, benefiting patients with limited treatment options. By offering both careful scrutiny and accelerated pathways, the FDA balances safety and innovation.
It continues to protect public health while ensuring that critical therapies are available when needed.


EMA (European Medicines Agency)
Unlike the FDA, the EMA is a regulatory agency serving multiple countries within the EU. It harmonizes the drug approval process across member states, making approvals easier. Once the EMA approves a product, it can be marketed throughout Europe. This centralization helps pharmaceutical companies streamline their operations across the region.
Additionally, the EMA works closely with global health organizations, particularly the WHO. Its alignment with international health initiatives ensures consistency in safety and efficacy standards.
The EMA’s collaborative approach strengthens its influence on global health policies. As the EU’s primary regulatory agency, it plays a key role in medical innovation.
By working with the WHO, the EMA helps improve global health standards and guidelines.
Moreover, this collaboration allows the agency to address emerging health challenges more effectively. With its shared goals and initiatives, the EMA contributes to advancing public health on a global scale.
WHO (World Health Organization)
The WHO plays a broader role in global health beyond drug regulation. It sets international standards for drugs, vaccines, and medical devices.
These standards help ensure safety and efficacy worldwide. Although the WHO does not approve drugs for specific countries, its influence is significant. National regulatory agencies often follow WHO guidelines when making approval decisions.
Additionally, the WHO helps regulatory agencies align their practices with global health goals. Its efforts ensure consistency across different countries and regions.
By setting these standards, the WHO strengthens global cooperation in healthcare. This collaborative approach helps address health challenges more effectively. As a result, the WHO plays a crucial role in improving health systems and ensuring better access to safe medical treatments worldwide.

Regulatory Agency Updates Pharma Professionals Must Know
The pharmaceutical industry is heavily impacted by updates from regulatory agencies. These updates influence everything from clinical trials to post-market surveillance.
New Guidelines for Drug Trials
Regulatory agencies have recently updated clinical trial protocols to increase patient diversity and improve trial accuracy.
Revised GMP Standards
New GMP standards now require stricter controls on data integrity and more robust documentation during production processes.
Focus on Environmental Impact
Agencies are now pushing for pharma companies to assess and mitigate the environmental impact of drug production and disposal.
More Stringent Labeling Requirements
Recent updates mandate clearer, more detailed labeling to ensure patients are fully informed about drug risks and benefits.
These updates directly impact how pharma professionals operate, making it crucial to remain updated on these changes.
Navigating the Future of Regulatory Agencies in Pharma
Greater International Harmonization
Regulatory agencies are working toward greater international harmonization to simplify drug approvals. They aim to create uniform standards that apply across multiple countries.
This approach helps pharmaceutical companies reduce delays and bring medicines to market faster. When agencies align their processes, they streamline approval timelines and improve efficiency.
As a result, patients gain quicker access to life-saving treatments. Additionally, harmonization reduces the need for duplicate testing, which saves time and resources.
With international cooperation, a drug approved by one agency may receive faster approval elsewhere. This collaboration strengthens trust between regulatory bodies and ensures consistent safety standards.
Countries can rely on shared data instead of conducting repetitive reviews. As more agencies adopt harmonized standards, pharmaceutical companies can expand into new markets more easily. This global alignment also benefits patients by increasing the availability of innovative therapies

Expansion of Digital Health Regulation
Regulatory agencies are expanding their focus on digital health as technology advances. They are introducing new guidelines for digital therapeutics, wearables, and health tech products.
These technologies offer innovative ways to monitor and improve patient health. However, they also require strict regulations to ensure safety and effectiveness. Agencies must address data security, accuracy, and patient privacy concerns.
As digital health grows, companies must adapt to meet these evolving standards.
This expansion creates both challenges and opportunities for pharma professionals. New regulations may require companies to modify product development and compliance strategies.
However, digital health also opens doors for innovation and improved patient care. Pharma professionals who stay informed about regulatory changes can gain a competitive advantage. Understanding these new guidelines will help them navigate approval processes smoothly.
As the industry embraces digital transformation, staying ahead of the curve will be essential. Those who adapt quickly will benefit from the growing digital health market.
Main Strategies in Regulatory Agency Updates
Accelerated Approval Pathways
Regulatory agencies introduce fast-tracking programs to speed up drug approvals for urgent medical needs.
Global Harmonization of Standards
Agencies align regulations across countries to streamline approvals and ensure consistency.
Increased Use of Real-World Evidence (RWE)
Regulators now consider real-world patient data to assess drug safety and effectiveness.
Stricter Data Integrity
New guidelines demand more detailed documentation and ensure compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Expansion of Digital Health Regulations
Agencies create rules for digital therapeutics, wearables, and AI-driven healthcare innovations.
Conclusion
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, regulatory agencies play a pivotal role in shaping the future of drug development, approval, and distribution. By staying updated on the latest regulatory agency guidelines, professionals can ensure compliance, foster innovation, and contribute to the global health landscape. The updates discussed in this article highlight the urgency of staying informed and proactive in navigating regulatory changes. With regulations constantly shifting, the need to stay ahead of the curve has never been more important for the pharma industry.
References

Ershad Moradi
Ershad Moradi, a Content Marketing Specialist at Zamann Pharma Support, brings 6 years of experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Specializing in pharmaceutical and medical technologies, Ershad is currently focused on expanding his knowledge in marketing and improving communication in the field. Outside of work, Ershad enjoys reading and attending industry related networks to stay up-to-date on the latest advancements. With a passion for continuous learning and growth, Ershad is always looking for new opportunities to enhance his skills and contribute to pharmaceutical industry. Connect with Ershad on Facebook for more information.

Master GxP Validation in 2026: Meaning, Key Steps, and Validated State Control
Auditors want evidence you can trace, not opinions you can explain. GxP validation links intended use, requirements, risk, and test results into one story. When you control changes and review performance, you keep the system inspection-ready every day on time.

Master GMP Compliance in 2026: Meaning, Core Elements, and How to Implement
GMP compliance keeps medicines safe, consistent, and traceable across every batch. This guide explains core GMP elements, practical rollout steps, and common pitfalls. It also shows how to strengthen training, documentation, data integrity, and audit readiness.

History of Pharmacovigilance: From the Thalidomide Crisis (1961–2026) to GMP Oversight
Thalidomide in 1961 changed drug safety forever. Since then, pharmacovigilance has grown from crisis response to proactive risk management. Today, teams track signals, tighten reporting rules, and connect safety data to quality systems. As a result, PV now links directly to GMP oversight, audits, and data integrity.




