Choosing between regulatory affairs vs quality assurance feels tough. However, clear facts make the decision easier. In many pharma markets, regulatory affairs (RA) mid-level roles often earn around USD 66,000–97,000 per year, with averages near USD 82,000. Meanwhile, quality assurance (QA) roles often sit around USD 51,000–87,000, with averages near USD 66,000.
Moreover, both paths lead to senior positions with six-figure salaries in large companies, especially in QA management. Yet money alone never tells the full story. You also need to think about daily tasks, skills, and long-term growth.
Therefore, this guide on regulatory affairs vs quality assurance explains responsibilities, skills, internships, education, salaries, and pros and cons. Additionally, it links these careers to broader pharma regulation topics, so you see where each role fits in the bigger system.
Understanding Regulatory Affairs vs Quality Assurance
Regulatory Affairs (RA) and Quality Assurance (QA) covers two sides of the same goal: safe, compliant medicines. RA teams manage the relationship with regulators. They translate laws into practical requirements and keep approvals valid. QA teams oversee systems inside the company. They protect product quality and make sure people follow procedures every day.
Moreover, RA focuses on external expectations, while QA focuses on internal execution. Together, they support inspections, approvals, and a strong quality culture.
In practice, many companies expect RA and QA to collaborate. For example, RA drives changes after new guidelines. QA then updates SOPs, trains teams, and checks process adherence. Therefore, both groups need strong communication and a shared mindset.
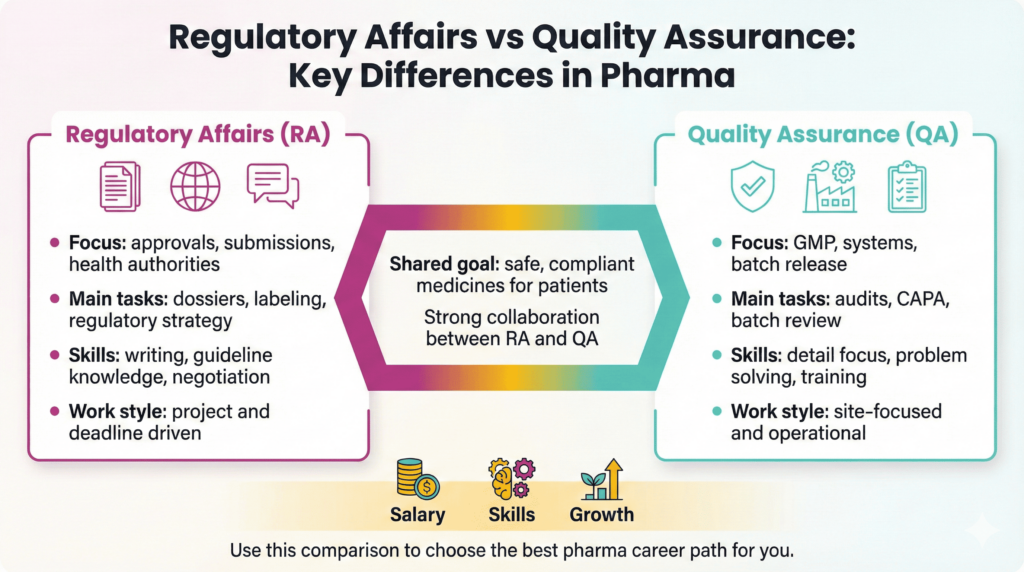
Key Responsibilities in Regulatory Affairs and Quality Assurance
You can understand these two career paths more easily when you compare tasks side by side. RA professionals concentrate on dossiers, variations, and contacts with agencies. QA professionals concentrate on systems, audits, and batch decisions.
Next, let’s break down the responsibilities for each function.
Regulatory Affairs Responsibilities
Quality Assurance Responsibilities
Regulatory affairs responsibilities in pharma usually include:
- Prepare, compile, and submit marketing authorization applications and variations.
- Track global guidelines and update internal requirements for new regions.
- Plan regulatory strategy for new products, line extensions, and lifecycle changes.
- Manage communication with health authorities and respond to questions or deficiencies.
- Coordinate labeling updates, artwork changes, and safety-related text revisions.
- Review promotional materials to ensure compliance with pharma regulation rules.
- Support inspections and answer regulatory-related queries during audits.
Moreover, pharma RA duties increasingly include digital systems, e-submissions, and regulatory intelligence tools.
Quality assurance responsibilities in pharmaceuticals typically include:
- Design and maintain the Pharmaceutical Quality System (PQS) and key SOPs.
- Approve batch records and make final release or rejection decisions.
- Lead deviation, CAPA, and change control processes across departments.
- Plan and execute internal audits and supplier audits.
- Oversee training systems and monitor GMP training effectiveness.
- Review validation and qualification documents for equipment, utilities, and processes.
- Monitor quality metrics and trigger improvements when trends appear.
Additionally, QA pharma responsibilities often cover cross-functional projects like data integrity, cleaning validation, and documentation improvements.
Regulatory Affairs Responsibilities
Regulatory affairs responsibilities in pharma usually include:
- Prepare, compile, and submit marketing authorization applications and variations.
- Track global guidelines and update internal requirements for new regions.
- Plan regulatory strategy for new products, line extensions, and lifecycle changes.
- Manage communication with health authorities and respond to questions or deficiencies.
- Coordinate labeling updates, artwork changes, and safety-related text revisions.
- Review promotional materials to ensure compliance with pharma regulation rules.
- Support inspections and answer regulatory-related queries during audits.
Moreover, pharma RA duties increasingly include digital systems, e-submissions, and regulatory intelligence tools.
Quality Assurance Responsibilities
Quality assurance responsibilities in pharmaceuticals typically include:
- Design and maintain the Pharmaceutical Quality System (PQS) and key SOPs.
- Approve batch records and make final release or rejection decisions.
- Lead deviation, CAPA, and change control processes across departments.
- Plan and execute internal audits and supplier audits.
- Oversee training systems and monitor GMP training effectiveness.
- Review validation and qualification documents for equipment, utilities, and processes.
- Monitor quality metrics and trigger improvements when trends appear.
Additionally, QA pharma responsibilities often cover cross-functional projects like data integrity, cleaning validation, and documentation improvements.
Regulatory Affairs Responsibilities
Regulatory affairs responsibilities in pharma usually include:
- Prepare, compile, and submit marketing authorization applications and variations.
- Track global guidelines and update internal requirements for new regions.
- Plan regulatory strategy for new products, line extensions, and lifecycle changes.
- Manage communication with health authorities and respond to questions or deficiencies.
- Coordinate labeling updates, artwork changes, and safety-related text revisions.
- Review promotional materials to ensure compliance with pharma regulation rules.
- Support inspections and answer regulatory-related queries during audits.
Moreover, pharma RA duties increasingly include digital systems, e-submissions, and regulatory intelligence tools.
Quality Assurance Responsibilities
Quality assurance responsibilities in pharmaceuticals typically include:
- Design and maintain the Pharmaceutical Quality System (PQS) and key SOPs.
- Approve batch records and make final release or rejection decisions.
- Lead deviation, CAPA, and change control processes across departments.
- Plan and execute internal audits and supplier audits.
- Oversee training systems and monitor GMP training effectiveness.
- Review validation and qualification documents for equipment, utilities, and processes.
- Monitor quality metrics and trigger improvements when trends appear.
Additionally, QA pharma responsibilities often cover cross-functional projects like data integrity, cleaning validation, and documentation improvements.
Skills Required for RA vs. QA
Skills Required for RA vs. QA
Regulatory affairs vs quality assurance also differs strongly in skills. However, both paths reward clear thinking and strong communication.
For RA roles, key skills include:
- Deep knowledge of guidelines (ICH, EMA, FDA) and submission formats.
- Strong scientific literacy to interpret clinical, non-clinical, and CMC data.
- Excellent writing skills for dossiers, responses, and labeling text.
- Negotiation and diplomacy for agency interactions and internal alignment.
- Strategic thinking for lifecycle planning and market expansion.
For QA roles, QA skills pharma employers seek include:
- Solid understanding of GMP and quality risk management.
- Detail focus for batch record review and documentation checks.
- Root-cause analysis and problem-solving for deviations and CAPAs.
- Training and coaching skills to support operators and supervisors.
- Confidence to stop production or reject batches when needed.
Moreover, both RA and QA roles require soft skills: resilience, teamwork, and the ability to explain complex rules in simple language.
Educational Background and Career Path for RA and QA
Both Regulatory affairs and Quality assurance paths usually start with a science or health degree. However, companies accept several backgrounds.
Common degrees for RA and QA include:
- Pharmacy, pharmacology, biochemistry and biotechnology.
- Chemistry, chemical engineering, or biomedical engineering.
- Sometimes nursing, medicine, or public health for advanced RA roles.
For RA, many professionals later add a specialized postgraduate diploma or master’s degree in Regulatory Affairs. Moreover, RA specialists often move from CMC, clinical, or QA into regulatory roles after some years.
For QA, early roles often start in production, QC, or microbiology. Then people move into QA officers, QA specialists, and QA manager positions. Over time, the Quality Assurance Career Path Pharma can lead to site quality head or global quality roles.
In both paths, continuous learning matters. Therefore, you should follow new guidelines, attend training, and collect certificates that show expertise.
Salary Expectations for each Career Paths
Salary expectations also shape the Regulatory affairs vs Quality assurance decision. However, ranges vary a lot by country, company size, and seniority, so use the numbers as general signals.
In many US markets, pharmaceutical Regulatory affairs roles often earn between USD 66,000 and 97,500 for typical mid-level positions, with averages around USD 82,000 per year. In contrast, many QA roles show averages near USD 66,000, with typical ranges from about USD 51,000 to 87,000.
Moreover, senior roles raise the ceiling in both paths. For example, QA managers in pharma can reach averages around USD 118,000 in the US, with top earners notably higher. Senior RA specialists and managers in mature markets such as Ireland also often sit in the EUR 50,000–60,000 band or above.
Therefore, you can treat RA as slightly more “strategic” and sometimes better paid at mid-level, while QA can deliver very strong salaries at management level. However, your performance, company type, and location still influence final numbers the most.
Pros and Cons of Regulatory Affairs vs. Quality Assurance
You now understand the basics of Regulatory Affairs vs Quality Assurance. Next, compare pros and cons to see which path fits your personality better.
Regulatory Affairs
Pros:
- Strong exposure to strategy and long-term product planning.
- Frequent contact with senior leadership and external regulators.
- Opportunities to work on global submissions and new launches.
- Clear RA career path from assistant to global lead.
Cons
- Tight timelines and high pressure during submissions and responses.
- Frequent guideline changes that demand constant study.
- Many hours at a screen reviewing complex documents.
Quality Assurance
Pros
- Direct impact on daily operations and product quality.
- Broad view across production, QC, engineering, and supply.
- Clear growth into QA lead, QA manager, and head of quality.
- Strong job stability because every site needs QA leadership.
Cons
- Tough decisions when you stop batches or reject products.
- Regular conflicts when you enforce rules under time pressure.
- Frequent audits, which some people find stressful.
Moreover, think about your own style. If you enjoy external rules, writing, and negotiation, RA may feel ideal. If you prefer shop-floor contact, troubleshooting, and systems, QA may suit you better.
Final words
Regulatory Affairs vs Quality Assurance both build strong, respected careers in the pharmaceutical industry. RA focuses on external approvals, guidelines, and strategy. QA focuses on internal systems, GMP, and daily product quality. Both paths need strong science knowledge, clear communication, and a commitment to patient safety.
Moreover, salary ranges for both functions look competitive, especially at senior levels. However, your happiness will depend more on daily tasks and culture than on a small pay difference. Therefore, reflect on whether you prefer documents and agencies or shop-floor reality and audits.
If you still feel unsure, combine internships, entry-level roles, and targeted courses. Additionally, you can explore pharma career paths that map RA and QA to other related roles like pharmacovigilance, validation, or quality control. Then you choose a path that fits both your skills and your long-term goals.
FAQ:
Choose regulatory affairs if you enjoy documents, guidelines, and strategic planning. You read regulations and design smart submission strategies. Choose quality assurance if you like shop-floor reality, problem solving, and coaching people. You review records, lead investigations, and build a strong quality culture.
RA vs QA salary ranges overlap, but mid-level RA often earns slightly more in many markets. Regulatory affairs specialists handle complex submissions, which can raise pay. However, QA managers and heads of quality often reach very high salary levels. The best choice still depends on your interests.
For RA roles, you need strong writing, guideline knowledge, and strategic thinking. You also handle negotiations with agencies. For QA roles, you need detailed focus, GMP expertise, and root-cause analysis skills. Both paths demand communication, teamwork, and resilience under pressure. Try Pharmuni and get more knowledge.
References:

Stephanie Männicke
Digital Marketing Especialist at Zamann Pharma Support, brings 8 years of experience in Corporate and Digital Communication. Specializing in Digital Marketing and Content Creation, Stephanie is currently focused on creating strategic content for Pharmuni's networks, especially content on topics such as recruitment, onboarding and employer branding. Outside of work, Stephanie is a mum, a crocheter and a movie fan. An avid reader and in search of expanding her knowledge, Stephanie is always looking for ways to innovate communication in the digital environment and connect people in a genuine way.

Master GxP Validation in 2026: Meaning, Key Steps, and Validated State Control
Auditors want evidence you can trace, not opinions you can explain. GxP validation links intended use, requirements, risk, and test results into one story. When

Master GMP Compliance in 2026: Meaning, Core Elements, and How to Implement
GMP compliance keeps medicines safe, consistent, and traceable across every batch. This guide explains core GMP elements, practical rollout steps, and common pitfalls. It also

History of Pharmacovigilance: From the Thalidomide Crisis (1961–2026) to GMP Oversight
Thalidomide in 1961 changed drug safety forever. Since then, pharmacovigilance has grown from crisis response to proactive risk management. Today, teams track signals, tighten reporting


