Recent FDA Form 483 and EU inspection trend analyses show that over 30% of repeat GMP observations stem from weaknesses already identified during internal audits but not effectively addressed. In many inspections, regulators cite the same gaps across multiple cycles, highlighting how poor audit follow-up directly increases compliance risk.
This reality confirms that a GMP audit is no longer a checkbox activity, but a critical tool for inspection readiness and compliance risk prevention. but critical tools for inspection readiness and risk prevention. As regulatory expectations rise, authorities increasingly assess how well organisations translate audit findings into sustained control under Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
In practice, a focused internal quality review helps manufacturers detect system weaknesses early, strengthen CAPA execution, and demonstrate control before inspectors arrive.
Table of Contents
What Is a GMP Audit and Why It Matters
A structured internal quality review is an independent assessment of quality systems, processes, and records to verify alignment with regulatory requirements. However, its true value goes beyond basic compliance confirmation.
Most importantly, quality system audits reveal how systems perform under routine pressure, not how procedures read on paper. Therefore, regulators often assess internal quality reviews when determining whether a site maintains ongoing control or relies on reactive fixes after inspections.
When audits function properly, they reduce inspection surprises and prevent repeat findings.
Types of GMP Audits
Quality system audits differ based on who performs them and the compliance objective they serve. Each audit type addresses a specific risk area within regulated manufacturing and quality systems, and together they form a complete audit framework that supports regulatory inspection readiness.
The main audit types covered in this section include:
- Internal Quality System Audits
- External Quality Compliance Audits
- Supplier and Vendor Quality Audits
- Regulatory Inspections and GMP Compliance Assessment
Internal Quality System Audits
Explain how internal audits evaluate day-to-day GMP compliance, test the effectiveness of quality systems, and identify gaps before regulatory inspections.
Cover points such as:
- Routine assessment of procedures, records, and practices
- Identification of systemic weaknesses and recurring issues
- Preparation of teams for regulatory inspection behavior and expectations
External Quality Compliance Audits
Describe audits conducted by third parties, partners, or clients to assess GMP compliance and quality system maturity.
Include focus areas such as:
- Independent evaluation of GMP compliance status
- Verification of quality agreements and responsibilities
- Early identification of gaps that may trigger inspection risk
Supplier and Vendor Quality Audits
Explain how supplier audits ensure that raw materials, services, and outsourced activities meet GMP requirements.
Highlight elements such as:
- Assessment of supplier quality systems and controls
- Evaluation of risk to product quality and supply continuity
- Use of audit outcomes to qualify, monitor, or disqualify suppliers
Regulatory Inspections and GMP Compliance Assessment
Describe inspections performed by regulatory authorities to verify compliance with GMP regulations.
Address points including:
- Evaluation of compliance against legal and guideline requirements
- Review of audit trails, investigations, CAPA, and change control
- Impact of inspection outcomes on licensing, enforcement actions, and regulatory trust
How to Plan an Effective GMP Audit
Effective compliance audits start with structured planning. Clear preparation improves audit consistency, reduces subjectivity, and strengthens regulatory inspection readiness. When organisations define scope, objectives, and risk priorities in advance, audits focus on areas that matter most for GMP compliance assessment rather than routine checklist activities.
Well-structured planning also helps quality teams identify system weaknesses early and address them before they escalate into inspection findings.
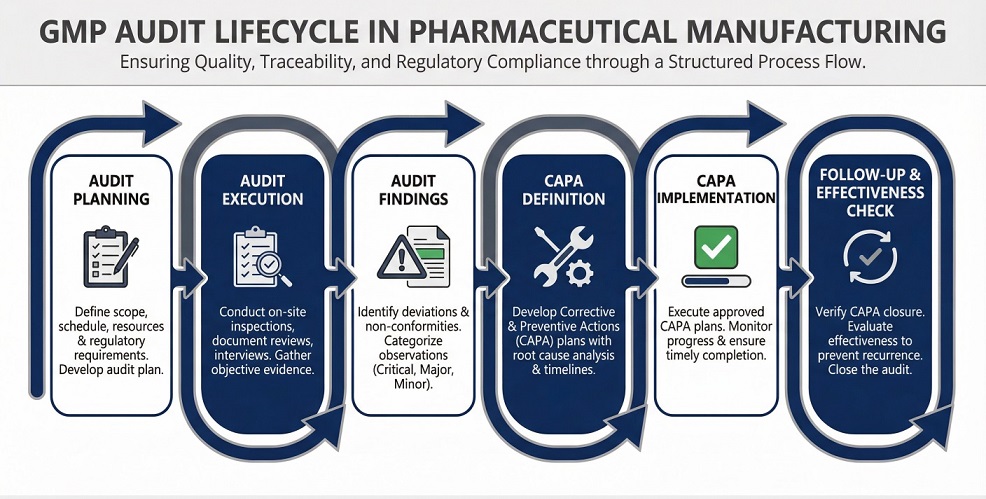
Audit Scope, Objectives, and Risk-Based Planning
Audit planning should clearly define what will be assessed, why it matters, and where audit effort should concentrate.
- Define audit scope based on processes, systems, sites, or outsourced activities
- Set audit objectives aligned with quality system risks and compliance expectations
- Prioritise high-risk areas using deviation trends and previous inspection outcomes
- Align audit focus with known inspection preparedness programs and enforcement risk areas
Audit Findings, CAPA, and Follow-Up
Quality system audits create value only when findings lead to effective corrective action. After audit execution, organisations must evaluate findings objectively and translate them into meaningful actions that address root causes rather than symptoms.
Effective follow-up includes prioritising findings based on risk, assigning ownership, and tracking audit findings and CAPA actions to completion. In addition, teams should verify CAPA effectiveness through follow-up audits, trend analysis, or targeted system reviews to prevent recurrence.
Consistent follow-up of audit outcomes strengthens regulatory inspection readiness and demonstrates that quality systems remain under control over time.
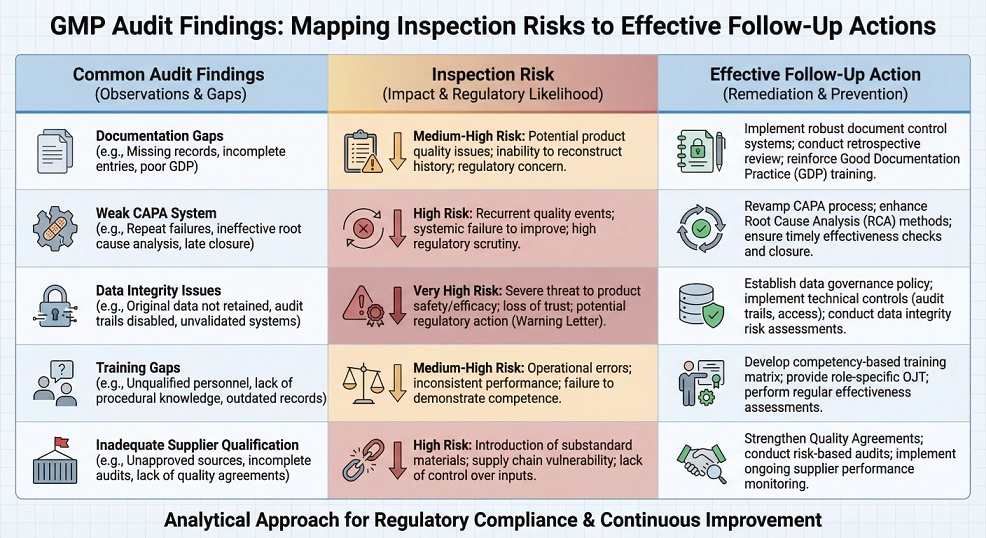
Key elements of effective follow-up include:
- Clear and risk-based root cause analysis
- Defined ownership with accountable timelines
- Verification of effectiveness under routine operating conditions
Without these elements, audits become administrative exercises rather than tools for sustained compliance and inspection readiness.
Final Words
Inspection enforcement data show that over 30% of GMP warning letters issued by the FDA reference repeat deficiencies linked to ineffective CAPA, many of which were already identified during internal reviews but not properly implemented. Similar EU inspection trend reports confirm that sites with weak audit follow-up often face the same observations across consecutive inspection cycles.
For this reason, a GMP Audit is not an internal formality or documentation exercise. Instead, it functions as a predictive compliance tool that tests whether quality systems truly operate under control, helping organisations reduce inspection risk and build sustained regulatory trust.
FAQs
Inspectors assess whether audit findings translate into meaningful CAPA actions across deviation handling, change control decisions, and batch disposition processes within regulated manufacturing sites.
Repeat observations usually occur when audits fail to identify systemic issues, prioritise high-risk processes, or prevent recurrence through effective CAPA in validated environments.
Because consistent follow-up shows that quality systems remain under control, address root causes, and respond proactively to trends rather than only during regulatory visits.
References
1-FDA Pharmaceutical Inspections and Compliance Guidance (FDA) U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Provides authoritative information on how the U.S. FDA evaluates GMP compliance, inspection processes, and use of Form FDA 483 during inspections.
2-Compliance with US and EU Internal Audit Requirements (BioPharm International) BioPharm International
Explains the role and regulatory expectations of internal audits/self-inspections under US and EU GMP, including quality system review requirements.
3-Good Manufacturing Practice Overview (EMA) European Medicines Agency (EMA)
Describes EU GMP fundamental principles, inspection planning, and the regulatory framework for manufacturers that must comply with GMP standards.

Mahtab Shardi
Mahtab is a pharmaceutical professional with a Master’s degree in Physical Chemistry and over five years of experience in laboratory and QC roles. Mahtab contributes reliable, well-structured pharmaceutical content to Pharmuni, helping turn complex scientific topics into clear, practical insights for industry professionals and students.

Visual Inspection in Pharma (2026): What It Is, Scope, PDF Guides and SOP Essentials
Visual Inspection checks parenteral units for particles, damage, and labeling errors before release. EU GMP Annex 1 expects inspection of parenteral containers (8.30) and warns visual inspection cannot replace integrity testing, including 100% testing for fusion-sealed volumes ≤100 mL (8.22).

GxP in pharma in 2026: How Inspectors Evaluate System Control
This article explains how GxP quality systems are assessed during inspections, why gaps in governance and execution lead to repeat audit findings, and how regulated pharma operations strengthen inspection readiness through risk management, data integrity, and lifecycle compliance controls.

Quality Oversight In 2026: Roles in pharma industry, GMP Expectations, And Risk-Based Control
Quality Oversight keeps GMP decisions consistent, traceable, and risk-based. It connects deviation handling, CAPA, change control, and trend reviews. It also proves management engagement through documented actions. Strong oversight reduces repeat failures and supports confident batch disposition.


