Deviation Reporting can stop a batch delay when a line-clearance miss becomes an audit finding. This guide covers GMP deviation investigation in pharma/biopharma only, not complaints or an OOS deep-dive. WHO TRS 986 (Annex 2) supports clear definitions, documentation, and investigation expectations today.
In pharma quality assurance, act fast: contain, capture evidence, batch records/logs, build a timeline, confirm impact, and write CAPA. WHO TRS 981 (Annex 2) ties QRM to deviation and investigation management, and WHO TRS 1044 (Annex 7) states deviations should be investigated and recorded. Trend repeats to cut recurrence and prove control.
Table of Contents
What Is Deviation Reporting
Deviation Reporting records any unexpected event that breaks a GMP process. Teams use it to protect patients, product quality, and compliance. It has 1 goal: find causes, fix issues, prevent repeats. You open a deviation when you see an error or clear missing step.
Therefore, start it fast, write facts, and attach evidence immediately.
-
Describe what happened, where, when, and who noticed it.
-
Assess impact on batch status, safety, and data integrity.
-
Document actions, assign owners, and set CAPA deadlines.

Why Deviation Investigation Matters in Pharma
Deviation investigation matters in pharma because it protects patients and product quality. It helps teams catch errors early and avoid batch delays. It also builds clear evidence for auditors and inspectors. You reduce repeat issues when you track trends and act fast. You aim for 1 result: reliable processes.
Therefore, use deviations to learn and improve, not to blame.
Document facts, evidence, and impact within the same shift.
Link each deviation to a root cause and CAPA plan.
Deviation Definition and Basics
A deviation is any unplanned event that breaks an approved GMP process. It can involve equipment, people, materials, methods, or data. You document deviations to protect patients and keep batches compliant. You also use them to learn and prevent repeat errors. One key rule: record the facts first, then investigate the cause.
Therefore, keep the basics clear and consistent for every deviation.
-
State what happened, where it happened, and when it happened.
-
Compare the event with the approved SOP, batch record, or spec.
-
Note immediate actions and decide the initial impact level.
What is a Deviation in GMP?
A GMP deviation is any unplanned event that breaks an approved process. It can impact product quality, data integrity, or patient safety.
Teams record the deviation as soon as it appears. Next, they capture facts, timestamps, and supporting evidence.
Deviation and It’s Reporting in Pharma Meaning in Pharma
Deviation and it’s reporting in pharma in pharma means documenting any unexpected GMP event. It captures what happened, when it happened, and where it happened. It also supports investigation and prevention.
Teams report deviations to protect patients and product quality. Then, QA reviews impact, risk, and required actions. Clear records help during inspections and audits.
Record the facts and attach batch records, logs, or photos.
Note immediate actions and assign owners for follow-up tasks.
Link root cause findings to CAPA and verify effectiveness.
Pharmaceutical Deviation Examples
Pharmaceutical deviations happen when a process drifts from the approved procedure. Teams report examples fast to protect patients and keep batches compliant every time.
-
Operator sets wrong mixing speed for 10 minutes.
-
QC logs show missing second-person verification on a critical entry.
-
A filter integrity test fails after setup.
-
Temperature logger records 3°C above limit in a cold room.
-
Line clearance leaves one rejected label on the table.
Small slips can trigger investigations and CAPA. Then, quarantine the affected materials. Use clear, factual notes and link each event to evidence.
Deviation vs Nonconformance vs Incident
Deviation report in pharma means documenting any unexpected GMP event. It captures what happened, when it happened, and where it happened. It also supports investigation and prevention.
Teams report deviations to protect patients and product quality. Then, QA reviews impact, risk, and required actions. Clear records help during inspections and audits.
Record the facts and attach batch records, logs, or photos.
Note immediate actions and assign owners for follow-up tasks.
Link root cause findings to CAPA and verify effectiveness.
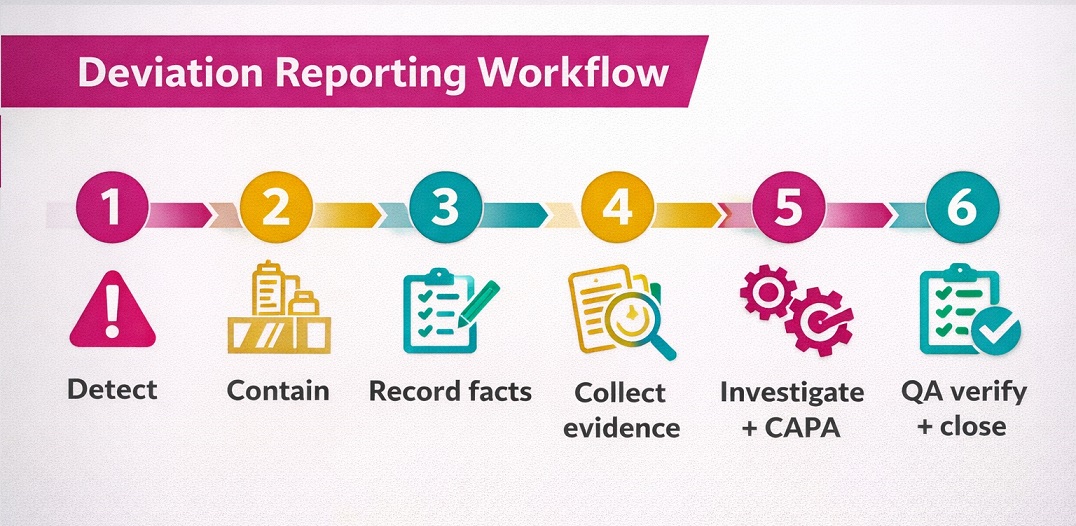
Deviation Report Workflow
Deviation Report workflow follows clear steps from start to closure. It begins when a team spots an unexpected GMP event. It ends after QA confirms control and learns are captured.
First, teams contain the issue and protect the batch. Then, they collect evidence and investigate root cause. Next, they define CAPA and set deadlines.
Open the deviation and describe facts, time, and location.
Assess impact, classify severity, and decide batch disposition.
Implement CAPA, verify results, trend repeats, and close.
How to Collect Evidence (Batch Records, Logs, Data)
Evidence collection starts at the moment the deviation appears. Quick action keeps facts clear and supports a strong investigation.
First, capture primary documents and system data before changes occur. Then, keep everything traceable with dates, times, and owners.
-
Copy the batch record pages linked to the event.
-
Save equipment logs, alarms, and maintenance entries.
-
Export raw data, audit trails, and system timestamps.
-
Take clear photos of labels, setups, or components.
-
Collect training records and relevant SOP versions.
-
Write a short timeline using confirmed times and sources.
How to Write a Deviation Report
A deviation report tells the story of a GMP event. It stays factual, clear, and easy to audit. It shows what happened and what actions followed.
First, write a short description with time, place, and batch details. Then, add evidence, impact assessment, and immediate actions.
-
Describe facts, not opinions, and use exact timestamps.
-
List evidence links: batch records, logs, data, and photos.
-
Document root cause, CAPA actions, owners, and due dates.
Deviation Report Templates and Forms
Deviation report templates help teams capture facts fast and consistently. They reduce missing details and speed up triage. Therefore, teams use one clear form across departments.
Good templates guide evidence collection and decision tracking. They support investigation, CAPA, and audit readiness. Teams also standardize terms to avoid confusion.
Deviation title, date, and location
Product, batch, and equipment ID
What happened and when
Immediate actions and containment
Risk rating and impact notes
Root cause summary and CAPA tasks
Approvals, attachments, and closure date
Final words
Deviation Reporting keeps GMP operations under control when mistakes happen. It protects product quality, patients, and compliance by recording facts, time, place, and impact. This article explains the workflow: open fast, contain the risk, collect evidence, investigate root cause, and close with traceable decisions.
Evidence matters because regulators expect objective support for conclusions. ICH Q9 (R1) ties risk management to deviations and investigations. ICH Q10 calls CAPA a key feedback system and requires effectiveness checks. In practice, human error causes over 80% of process deviations, so strong CAPA must prevent recurrence, not just explain it.
FAQs
Open it as soon as the GMP event appears. Capture the time, place, batch, and facts early. This supports reliable decisions and traceability.
A deviation starts inside operations when a process step goes off-plan. A complaint starts from the market or customer. An OOS focuses on test results outside specifications and follows its own investigation path.
Prioritize objective records linked to the event: batch records, equipment logs, alarms, raw data, and audit trails. Then add a clear timeline that matches those sources.
References

Ershad Moradi
Ershad Moradi, a Content Marketing Specialist at Zamann Pharma Support, brings 6 years of experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Specializing in pharmaceutical and medical technologies, Ershad is currently focused on expanding his knowledge in marketing and improving communication in the field. Outside of work, Ershad enjoys reading and attending industry related networks to stay up-to-date on the latest advancements. With a passion for continuous learning and growth, Ershad is always looking for new opportunities to enhance his skills and contribute to pharmaceutical industry. Connect with Ershad on Facebook for more information.

Pharmaceutical Warehouse in 2026: GMP Storage Requirements Guide
Effective drug storage compliance depends on validated storage conditions for pharmaceuticals, structured segregation control, and reliable batch traceability in warehouse operations. This guide explains how temperature excursion management and GDP compliance warehouse practices strengthen inspection readiness and regulatory defensibility.
GMP Interview in 2026: Questions and Answers with Audit Insight
More than 60% of regulatory observations in pharmaceutical manufacturing relate to documentation control, investigation quality, and procedural compliance gaps. GMP Interview preparation in regulated environments determines whether a candidate can operate safely under inspection pressure.

Harmonization in pharmacovigilance in 2026
Inspection trends show that inconsistent global safety practices remain a leading source of pharmacovigilance findings. This article explains how regulatory harmonization, aligned safety reporting, and coordinated oversight shape inspection outcomes and support compliant international pharmacovigilance operations.